2. Einführung¶
Willkommen beim Mahara Nutzerhandbuch. Dieses Handbuch stellt Ihnen jederzeit Informationen zur Nutzung von Mahara zur Verfügung. Es informiert Sie darüber welche Bedeutung und welche Möglichkeiten die verschiedenen Funktionen haben, die Sie auf Ihrem Bildschirm sehen.
Lassen Sie uns direkt anfangen.
2.1. Was ist Mahara?¶
If you’re wondering what Mahara or an ePortfolio is, why you might want one and what it can do for you, then read on. You’re about to find out.
At the simplest level, Mahara is two things: an ePortfolio and a social networking system combined. An ePortfolio is a system in which students can record „evidence of lifelong learning“ – such as essays, artwork or other such things they produce that can be stored digitally. Such things are known as artefacts in Mahara. Social networking systems need little introduction – think Bebo, Facebook or MySpace (back in the old days). Basically, they give a way for people to interact with their friends and create their own online communities.
But Mahara is much more than just a place to store files. Mahara also includes blogging, a résumé builder, and web services to integrate with other platforms.
Bemerkung
Here’s a short video by Domi Sinclair, formerly at University College London. She explains what Mahara (called „MyPortfolio“ at UCL) is and for what it can be used.
2.2. Using a metaphor¶
It often helps to use a metaphor to explain a new concept. There are many metaphors used for portfolios. Here are two of them to give you an idea of how you could explain portfolios to your learners.
Bemerkung
Kate Coleman explores the idea of using metaphors for portfolio work in her PhD thesis.
Would you use any of these metaphors? Do you have your own?
2.2.1. The gallery or museum¶
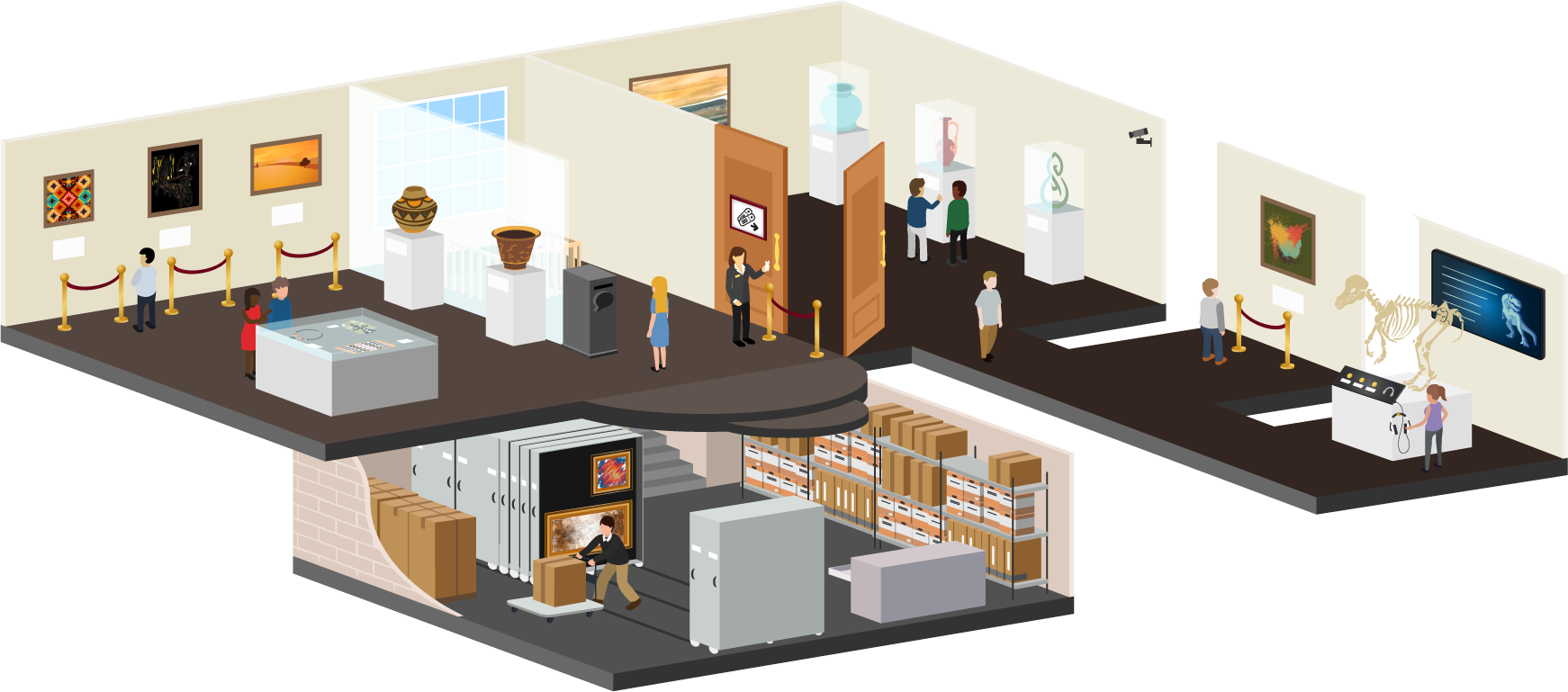

The gallery or museum metaphor¶
Bemerkung
This metaphor is used by Mandia Mentis at Massey University in New Zealand. She shared her idea in the Mahara Newsletter January 2018.
The basement is the common storage space of all the artefacts that the gallery owns or has leased. Artefacts are organized and catalogued to be found more easily later on when they are needed. A curator may shuffle artefacts around and add new ones as they come in. There is constant movement as artefacts are acquired, catalogued, brought up to the gallery for an exhibition, or returned to storage when a particular exhibition has finished.
The different media are used as artefacts. They can be text, images, audio, video, sculptures, or a mix of them.
The exhibition spaces can be small or large and are centred around a common theme each. The curator selected the artefacts to be shown carefully for the story that they want to tell. Not all artefacts that the gallery owns on a particular topic are exhibited so as not to overwhelm the viewer. Sometimes only one or two pieces represent a larger body of work.
The curator provides insight into the collection by adding explanatory notes, meta information, and also interpretation to the artefacts for the viewer to be guided through the exhibit and made aware of the differences between the artefacts.
Some of the exhibits are closed to the general public and require either an entrance fee or prior approval. In those cases, only authorized persons can enter the exhibit and view the artefacts.
Viewers wander the gallery on their own or in groups and point out what they see or feel, discuss the artefacts and the wider collection, and engage with the curator or even the artists in discussions. They leave feedback or sign a visitor book to voice their opinion. They also overhear other people talking about the artefacts and learn from these interactions.
Some of the exhibits are permanent while others are temporary allowing people to come back as often as they like or only during a specified time frame. At any time that they are in the exhibits, they can leave feedback, draw their own conclusions, and learn from the artefacts and the interpretations that they have seen.
The gallery’s management team wants to keep everyone safe and also gather data which exhibits are the most popular, when people are coming to the gallery and how often, and what it costs to keep the gallery running. The team runs regular reports and makes changes to the gallery as a result of that.
This translates to:
Basement: Mahara content area where you can upload files and create other learning evidence such as journal entries, plans, notes, etc.
Artefacts: The pieces of learning evidence that illustrate a skill gained, a competency accomplished, a step made in a longer process or material referenced for learning purposes.
Organizing and cataloguing: Putting files into folders and using tags on artefacts to retrieve them again later on.
Curator: Portfolio author
Exhibition spaces: Portfolio pages (small portfolios) or portfolio collections (large portfolios consisting of multiple pages).
Insight into artefacts: Reflections and explanatory commentary.
Entrance fee / prior approval: Assigning access permissions to portfolios based on who should be allowed to view the particular page or collection.
Viewers: Portfolio Viewers; they can come on their own or in groups.
Permanent / temporary: For how long the portfolio is available. Some portfolios may only be shared for a short amount of time with somebody else.
Management team: The people running the site and offering the service.
Feedback: Feedback left and comments made by viewers on someone’s portfolio, reflections or learning evidence.
2.2.2. The performance¶
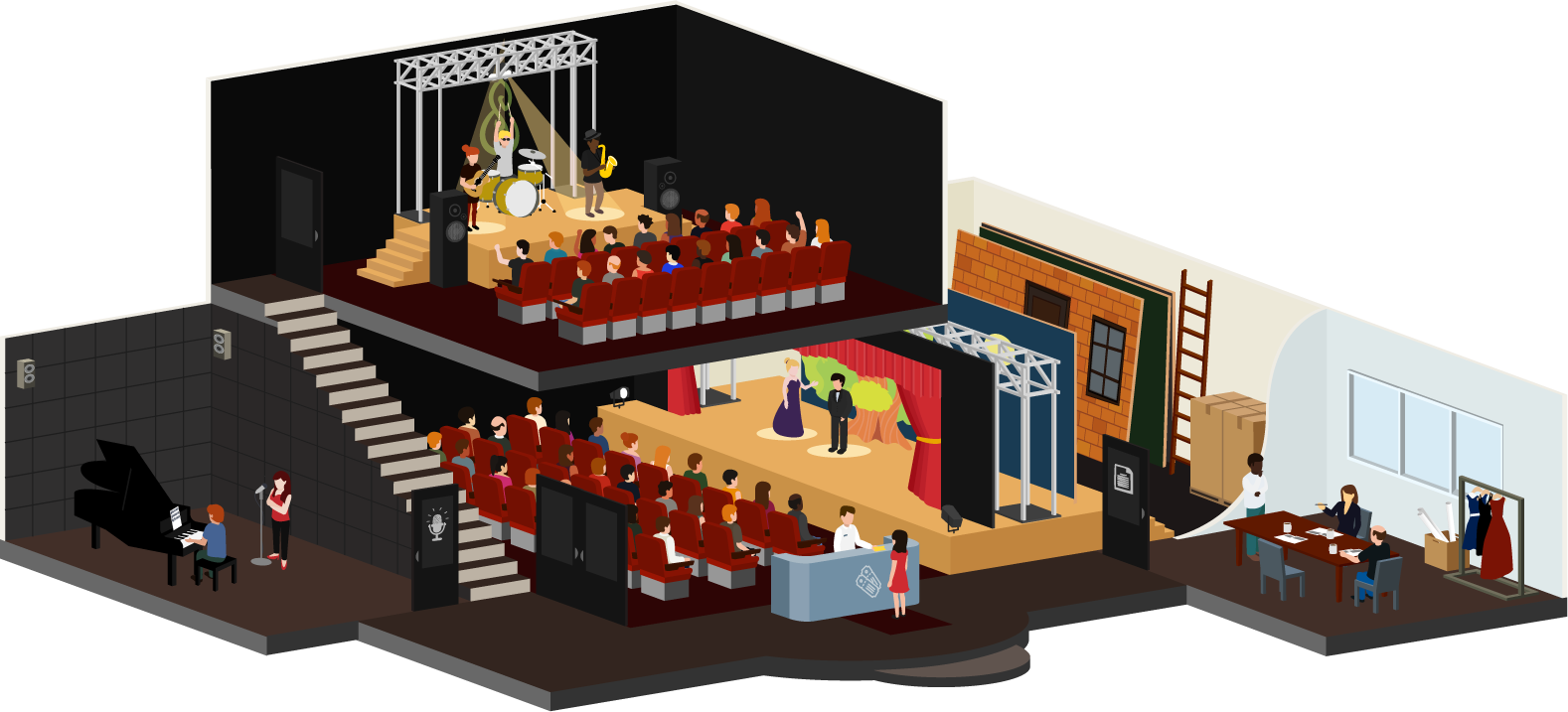

The performance metaphor¶
Bemerkung
This metaphor was introduced by Hazel Owen on her website. She shared her idea in the Mahara Newsletter January 2018.
An important aspect in this metaphor is the human element and that activities happen in communities and are not just things. In the performance metaphor we see that people interact in all matters from the preparation to the final performance and learn from each other.
In the backstage area, projects are discussed and conceptualised, changed, and finalised. A team is often involved in these processes giving feedback, and inviting newcomers / apprentices to try things out and learn from more experienced staff.
Depending on the director, a performance in one theatre may vary widely from that in another as a play can be interpreted many different ways, kept in its classic form, modernised or completely re-imagined. It is up to the company to settle on their interpretation and the way forward, which can include changes to the language, the mood, the back drops, and props used during the performance.
The backstage is only accessible to a group of authorised staff. Outsiders need a pass to be invited into this space.
Rehearsals play a fundamental role when preparing for a performance as they give the performer the time to practice their art, receive feedback from a teacher or also peers. They can practice in a safe space that is not accessible to an audience and thus don’t have to fear premature comments that would only be based on a small extract of the performance rather than its entirety.
Once the performance is deemed to be ready to be shown, often a dress rehearsal is scheduled to invite a select group of people for feedback and giving the troupe a chance to make final adjustments before the show is taken live.
Many different performances can take place within a building attracting different audiences, which in turn have different experiences that they bring to the events and see them through different eyes.
Some performances may require an entrance fee whereas others can be free. Some may also invite people to participate more fully in the performance itself rather than only sit and watch.
In Mahara this translates to:
Backstage: Artefact upload and creation and portfolio setup space before the learning evidence is shared with a wider group; portfolios can be created by individuals or in groups collaboratively.
Interpretations: Personalisation of each portfolio author in how they want to display their learning evidence, reflections, etc.
Rehearsals: Access given to a teacher or peers for feedback; not a one-time thing but iterative and supports growth of the portfolio author
Different performances: Being able to set up a variety of portfolios that serve different purposes and may or may not be connected
Entrance fee: Access permissions governing who can see which portfolio
2.3. Das Mahara-Konzept¶
In Mahara kontrollieren Sie selber welche Informationen Sie in Ihr Portfolio einstellen und anderen Personen zugänglich machen. Diese Informationen oder Materialien werden als Artefakte bezeichnet. Um den Zugang zu diesen Artefakten festzulegen, werden die Artefakte in Bereichen von Ihnen angeordnet. Diese bezeichnet Mahara als Ansicht. Sie können beliebig viele Ansichten erstellen. Jede Ansicht kann von Ihnen frei gestaltet werden und einzelne oder viele Artefakte enthalten. Wie Sie Ihre Ansichten gestalten, hängt von Ihren Absichten und den Zielgruppen ab. Sie können einzelnen Personen, einer Gruppe oder der Öffentlichkeit Zugriff auf Ihre Ansichten geben.
Einige Beispiele, was Sie in Mahara erstellen können:
eine Seite für Ihre Freunde oder Familie mit Urlaubsbildern und einem persönlichen privaten Blog
eine Seite für Ihre/n Tutor/in mit Aufgaben und einer Lernprozessreflexion
eine Präsentationen Ihrer besten Arbeiten und Ihr Lebenslauf für potenzielle Arbeitgeber
…
Ihr Portfolio kann aus einer einzelnen Ansicht oder einer Sammlung von Ansichten bestehen. Artefakte, die in einer Ansicht platziert werden, sind zunächst nur für Sie selber sichtbar. Jedes Artefakt wird nur einmal von Ihnen angelegt. Danach kann es in beliebig vielen Ansichten von Ihnen verwendet werden.
Stellen Sie sich vor, dass Sie alle Artefakte in einem Schuhkarton gesammelt haben. Immer wenn Sie ein neues Artefakt erstellen, legen Sie es in den Karton. Wenn Sie nun beginnen, Ihr Portfolio zu erstellen, greifen Sie in den Karton und wählen die Artefakte aus, die Sie verwenden möchten. Jetzt müssen Sie die einzelnen Artefakte in Ihrem Portfolio nur noch so anordnen, wie Sie es sich vorstellen.
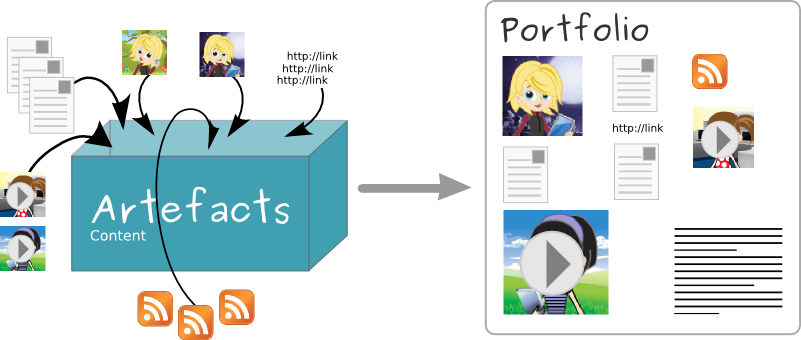
Portfolioarbeit mit Mahara¶
Das Diagramm unten mit Beispielartefakten, Ansichten und Gruppen zeigt wie Inhalte mit anderen geteilt, in verschiedenen Kontexten wiederholt genutzt und für unterschiedliche Zielgruppen eingesetzt werden können.
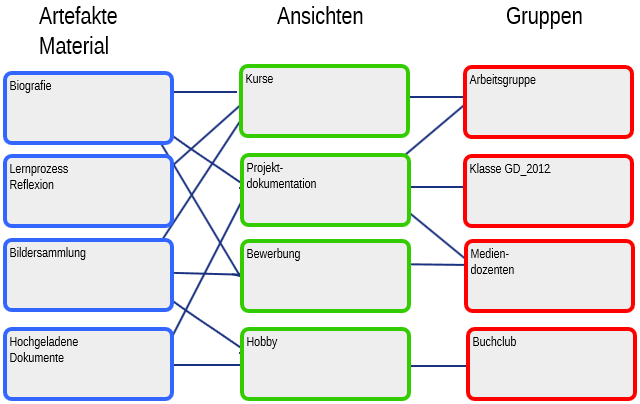
Das Mahara-Konzept¶
2.4. Wie passt Mahara in die Landschaft des eLearnings?¶
If you think of LMSs such as Moodle, Canvas, and Blackboard as the formal, structured side of e-learning, then Mahara is the social, reflective side. An LMS and an ePortfolio complement one another in an online learning environment.
In particular, while Mahara’s APIs are open to all, Mahara can integrate with Moodle natively to provide a streamlined user experience. This is not limited to SSO via MNet. Students are able to export assignments, blogs and much more straight into Mahara to use as artefacts, which can then, of course, be placed into pages.
2.5. Und wenn ich eine Funktion benötige, die in Mahara nicht existiert?¶
Mahara has been designed from the ground up to be an open, pluggable system. Creating new artefacts, authenticating against a custom system and much more can be implemented simply through writing a plugin that uses the appropriate core API. What this means is that it is free and easy for you to customise almost anything about Mahara to suit your needs. Paid support is available through a network of Mahara Partners should you require it.
2.6. Und wie geht es weiter?¶
Sie haben nun eine grundlegende Vorstellung darüber, was Mahara ist. Sie können nun:
Eine Liste der Features von Mahara lesen.
Explore the demo or download Mahara for yourself to play with.
Sign up to the mahara.org community and begin asking questions and contributing in the forums.
Diese Anleitung weiter lesen.
2.7. Wo erhalte ich Ideen, wie ich Mahara nutzen kann?¶
The Mahara newsletter features individuals and institutions and their use of Mahara. You can subscribe to it or read it online. It is published four times a year, and you can contribute your ideas as well.
You may wish to check the list of books or papers that have been published on Mahara or what users talk about in conference presentations.
2.8. Wo Sie Hilfe bekommen¶
Contextual help is available throughout Mahara via the Help icon . Click on it to find out more about the action you are about to perform.
Stellen Sie Fragen in den Foren.
2.9. Mahara und Barrierefreiheit¶
Mahara aims to be usable by as many individuals as possible, including those with disabilities or special needs. Creating accessible web content is a requirement in many countries. In order to provide international guidelines, the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) were created. There are three conformance levels under the WCAG 2.0, the latest edition of the guidelines: A, AA, and AAA. Each level requires conformance with previous levels and includes its own specific guidelines for how websites should be made accessible.
With version 1.9, Mahara has reached level AA for user-facing areas of the system. The administration of Mahara is predominantly on level AA as well. We endeavour to keep up level AA to continue to provide good navigation of the site to everybody.
The Mahara project can only control the accessibility of the navigation and overall platform. People uploading or creating content are responsible themselves to make their content accessible.
Wenn Ihnen ein Problem mit der Barrierefreiheit begegnet, erstellen Sie bitte einen Bericht im Bug-Tracker und vergeben Sie das Schlagwort „accessibility“.
Wenn Sie ein Screenreader-Nutzer sind, können Sie den folgenden Zugangsschlüssel benutzen, um die Elemente des Hauptmenüs in Mahara zu steuern:
Reguläre Nutzer-Oberfläche:
d:Dashboard
i: Inhalt
p: Portfolio
g: Gruppen
a: Administration
Administrator-Oberfläche:
a: Admin Home
k: Site konfigurieren
n: Nutzer
g: Gruppen
i: Institutionen
e: Erweiterungen
2.10. Welche Version von Mahara habe ich?¶
Wenn Sie keinen Zugang zum Administrationsbereich haben, können Sie nicht sofort erkennen, welche Version von Mahara Sie benutzen. Wenn man die Maharaversion kennt, hat man jedoch einige Vorteile:
Sie können sich vergewissern, dass Sie sich auf das richtige Benutzerhandbuch beziehen.
Sie können herausfinden, ob Sie eine aktuell unterstützte Version von Mahara benutzen oder mit einer älteren Version arbeiten.
Wenn Sie mit einer älteren Version von Mahara arbeiten, können Sie das Benutzerhandbuch nach neuen Funktionen durchsuchen.
Wenn Sie einen Programmfehler melden wollen, werden Sie häufig nach der genauen Version von Mahara gefragt, in welcher Sie das Problem bemerkt haben.
Sie können ganz einfach herausfinden mit welcher Version von Mahara Sie arbeiten, indem Sie sich den HTML Code der Site anschauen. Keine Angst, es ist nicht so schlimm wie es sich anhört.
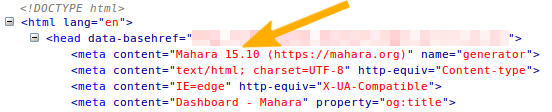
Der HTML Code zeigt die Nummer der Maharaversion an¶
Firefox und Chrome / Chromium:
Klicken Sie in Ihrem Browser mit der rechten Maustaste auf eine beliebige Seite in Mahara.
Wählen Sie die Option „Seitenquelle anzeigen“.
Schauen Sie nach dem Meta-Schlagwort „Erzeuger“.
Safari:
Machen Sie das „Menü ausgestalten“ sichtbar: Safari → Voreinstellungen → Erweitert→ wählen Sie „Menügestaltung in der Menüleiste anzeigen“ aus.
Klicken Sie mit der rechten Maustaste auf eine beliebige Seite in Mahara.
Wählen Sie die Option „Seitenquelle anzeigen“.
Schauen Sie nach dem Meta-Schlagwort „Erzeuger“.
Bemerkung
Only the major version number of Mahara is displayed for security purposes. The minor version number is only visible to the administrator on Administration menu → Admin home. We recommend you keep Mahara up-to-date with security updates to ensure that your instance is not vulnerable to known security issues.