11.8. Extensions¶
Administration menu → Extensions
Note
Extensions is only accessible by site administrators.
Extensions in Mahara serve to provide certain functionality in the system. Extensions can be installed at any point and can also be hidden.
11.8.1. Plugin administration¶
Administration menu → Extensions → Plugin administration
The Plugin administration lists all the plugins that are currently installed on your Mahara instance and provides a link to the plugin configuration settings where available.
Plugins in Mahara are always installed and can be accessed if people know the URLs and would otherwise have access. Rather than enabling and disabling the functionality, plugins are hidden or made visible by clicking on the Hide or Show buttons beside the plugins. When hiding an artefact type plugin, Mahara stops the display of the blocks related to it as well.
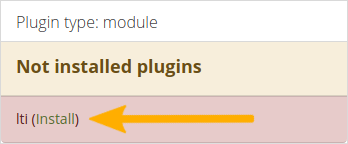
Warning when a plugin is not yet installed¶
If you added a plugin to your site’s codebase or if a new plugin was added to Mahara since the last upgrade that you performed, you will need to install it. A plugin that is not yet fully installed is marked with a warning and listed first in its section. Click the Install link to start the installation process.
In order to delete a plugin completely, you must delete the code and all database tables that pertain to the plugin. Additionally, you need to delete it from a number of system tables, e.g. ‘artefact’, ‘artefact_config’, ‘artefact_cron’, etc. View more information on how to uninstall a plugin.
Note
Core Mahara functionality can be made unavailable to account holders by hiding it. This may be useful if you connect Mahara to another system that already provides this functionality or if you do not wish people to use that functionality. However, the decision about hiding a functionality should be considered thoroughly as it may also mean that people may not be able to have as many artefacts available to them as they could have.
If a particular default plugin has been deprecated, an alert is displayed on an upgraded site to alert the site administrator to that change.
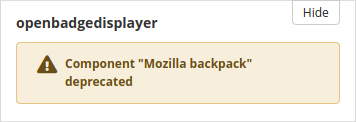
Alert when a plugin has been deprecated¶
In the following, only the plugins that have additional settings are discussed.
11.8.1.1. Blocktype¶
You can decide in which order the block types are listed in the block configuration when you put a block onto a page.
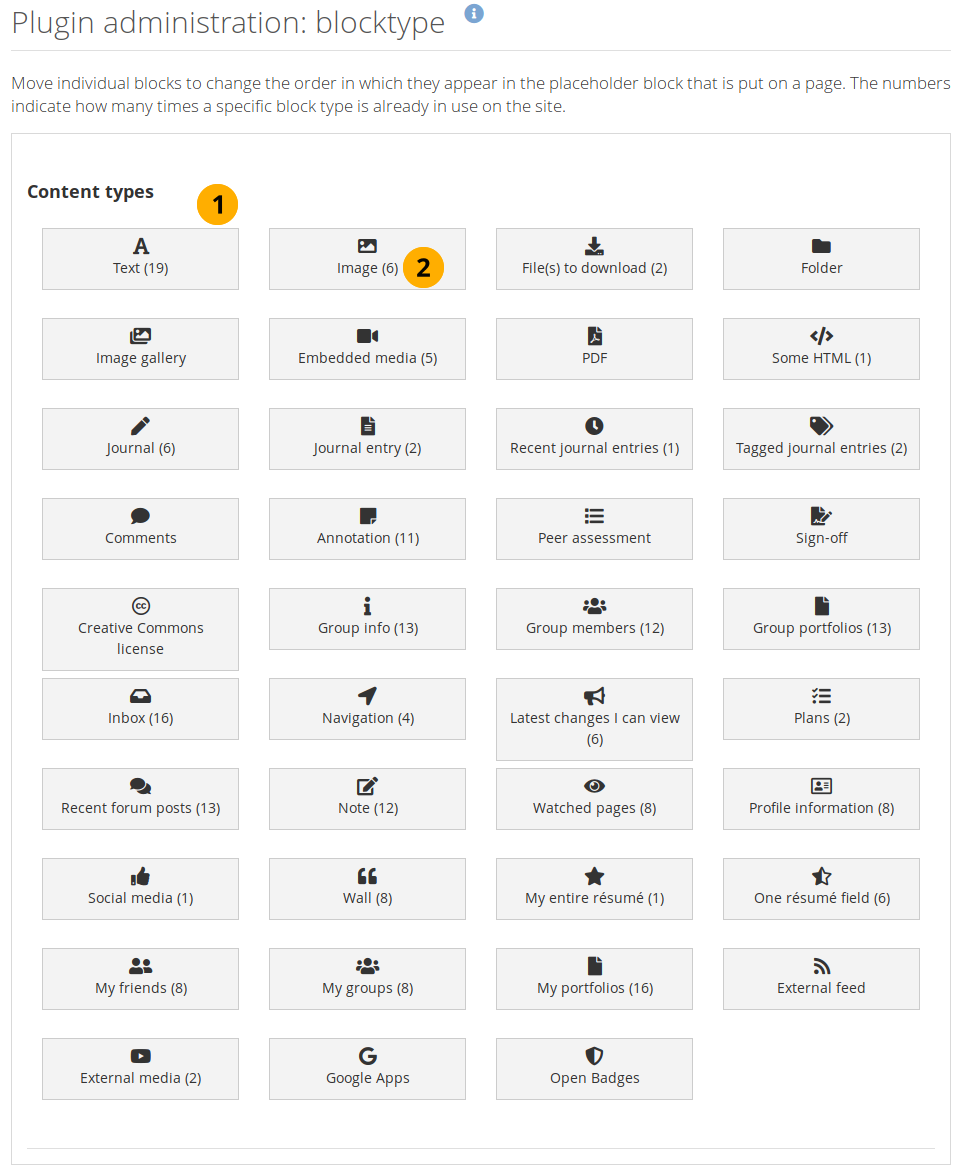
Order the block types for display in the placeholder block configuration¶
All block types that are available in Mahara are listed. You may not put all onto every page as their usage depends on the page context. Drag and drop the blocks to change their order.
Note
Typically, the first four blocks are displayed in the placeholder block configuration by default. Other blocks are accessible by clicking the Show more button.
This allows you to give quick access to the four most widely used blocks. Alternatively, you could pull blocks higher up that are underused.
The number indicates how many times this block has been used on the site.
Note
Some blocks are automatically placed on all profile and dashboard pages or group homepages.
11.8.1.2. Blocktype: File / folder¶
You can decide the default sort order for files displayed in a Folder block and whether viewers of portfolio pages that contain a Folder block should be able to download the contents of the folder as zip file in one go.
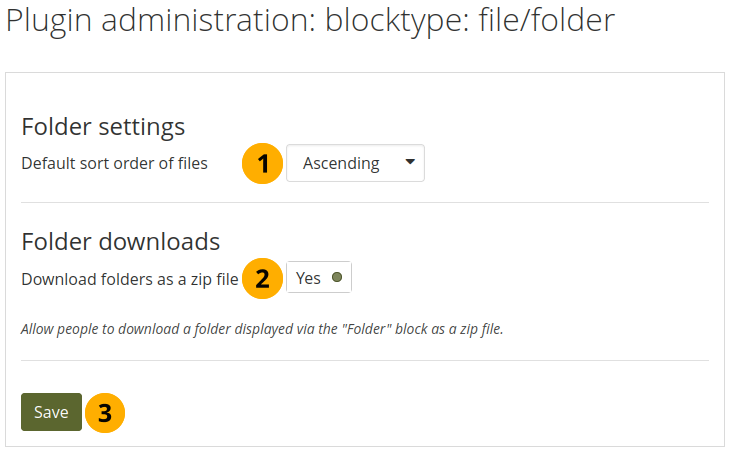
Configure the Folder block¶
Default sort order of files: Decide whether the default sort order for displaying files in a Folder block should be alphabetically ascending or descending.
Note
Page authors can change the sort order for each block.
Download folders as zip files: Switching this option to ‘Yes’, you can download the contents of a folder displayed in a Folder block as zip file.
See also
Site administrators decide in the Artefact type: File settings for how long the zip file is kept on the server.
11.8.1.3. Blocktype: File / gallery¶
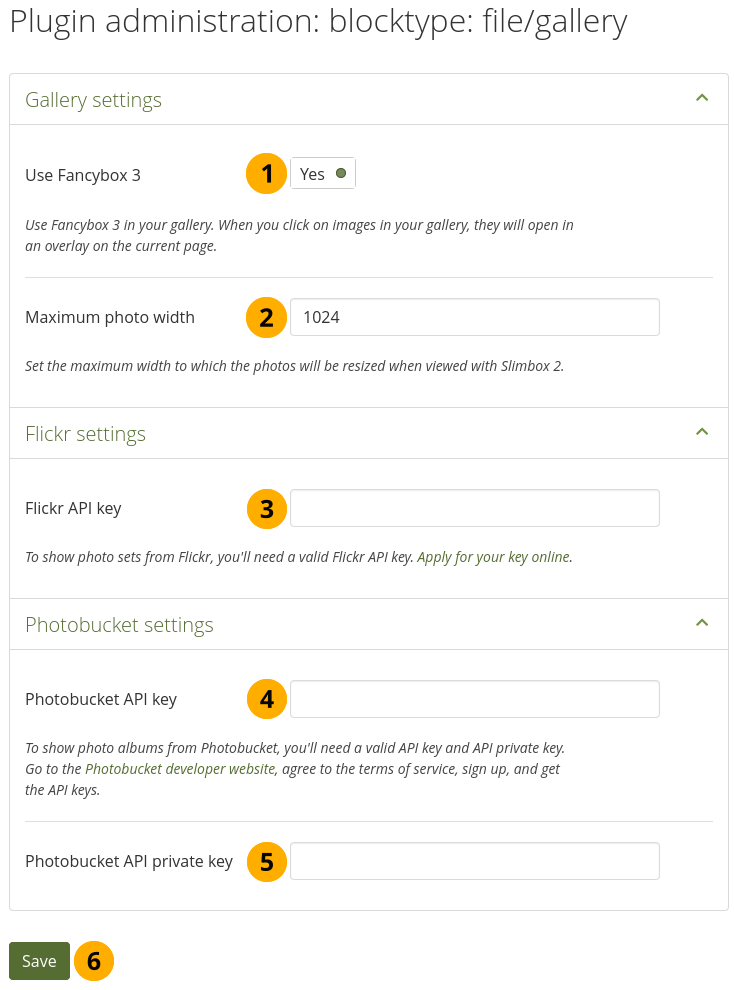
You can provide additional image gallery settings and also allow authors to make Flickr and Photobucket image galleries available. The settings you make on this page will be the default settings for everyone.
Configure the Image gallery block¶
Use Fancybox 3: Switch this option to ‘Yes’ if you want to enlarge images from your image gallery on the page in an overlay instead of opening them in a new window.
Maximum photo width: Set the maximum width (in pixel) to which the photos will be resized when viewed with Fancybox.
Flickr API key: If you want to allow authors to display photos from Flickr, you need a valid Flickr API key. You can apply for the key at Flickr.
Photobucket API key: If you want to allow authors to display photos from Photobucket, you need a valid API and private API key. You can get them from the developer page of Photobucket.
Photobucket API private key: Provide the private API key from Photobucket that you will have received.
Click the Save button to keep your changes.
11.8.1.4. Blocktype: File / internalmedia¶
Configure which file types people can embed into the Embedded media block. If you disable a file type that has already been used in a block, it will not be rendered any more.
Mahara comes with Video.js, a media player that can play a number of media files and does not require Flash (though it does have a Flash fallback option). Other video file types can be enabled, but people must have the appropriate software installed on their computers and the respective plugins enabled in their browsers to play them.
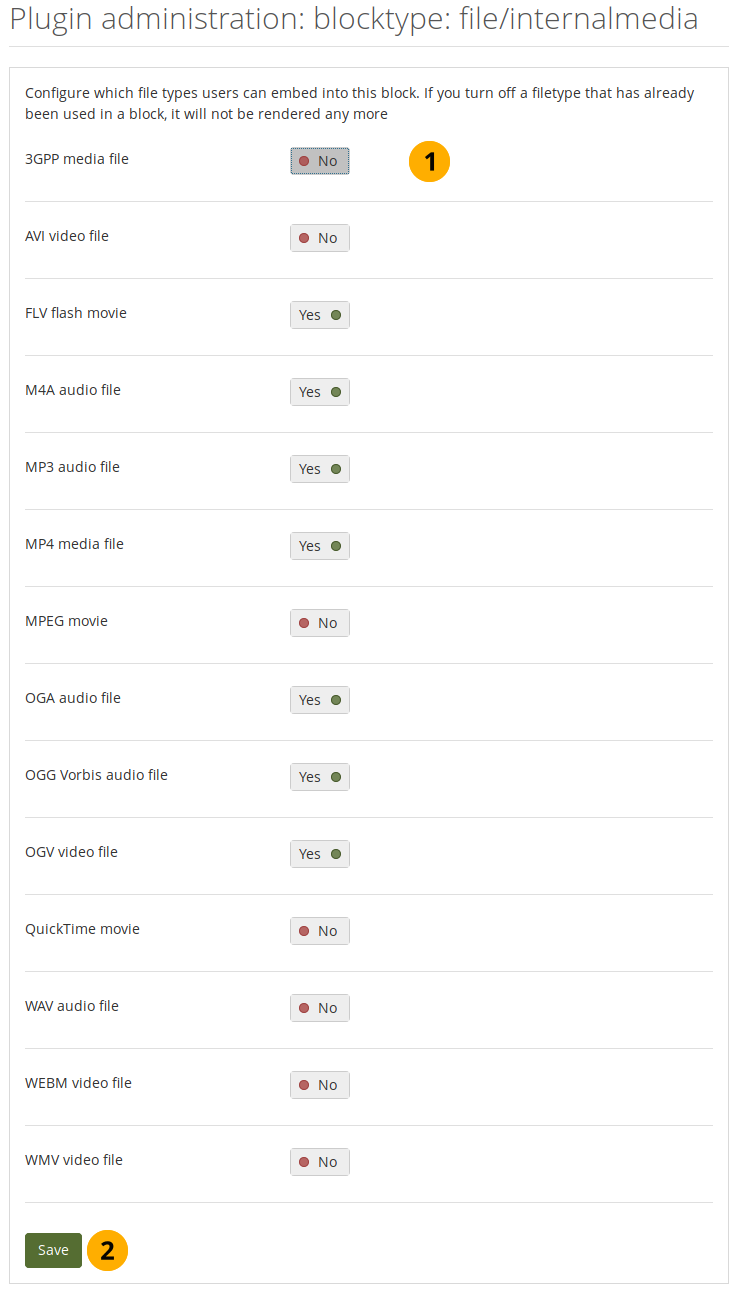
Configure the Embedded media block¶
Turn on the file types that you wish authors to be able to show on their portfolio pages.
Click the Save button to keep your changes.
Note
If you allow the embedding of file types that cannot be played by Video.js, some people may not have the necessary software installed for displaying these file types.
Here’s an overview of the video and audio file formats that can be played by Video.js and which browsers can view them. Only because Video.js supports them does not mean that all browsers can play them. They still need to support a specific file format themselves. Listed are only the browsers that Mahara supports. For updates to browser support, check the site ‘Can I use…’.
iOS devices may not always display MP4 files as the devices may only recognize the MPEG4 ‘Baseline’ profile rather than the ‘High’ profile. You can read the Apple specifications and convert a video if needed using Handbrake. Newer iOS devices (from the iPhone 5S on) should play ‘High’ profile videos.
File format |
Chrome |
Chrome for Android |
Firefox |
Internet Explorer / Edge |
Opera |
Safari (incl. iOS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3GPP media file |
||||||
FLV Flash movie (requires Flash) |
||||||
M4A movie |
||||||
MP3 audio |
||||||
MP4 video (H.264) |
||||||
MPEG movie |
||||||
OGA audio |
||||||
OGG Vorbis audio file |
||||||
OGV video |
||||||
WAV audio |
(Edge) |
|||||
WEBM video file |
Note
While you can upload any file fromat from any computer or Android device, you are not able to upload audio files from an iOS device. You can only upload MOV video files. These require a browser plugin to be played and are not served via Video.js.
AVI and WMV files can only be played on computers running Windows unless you have a browser plugin installed on another operating system.
11.8.1.5. Blocktype: Text¶
You can convert Note blocktypes to Text blocktypes across the entire instance.
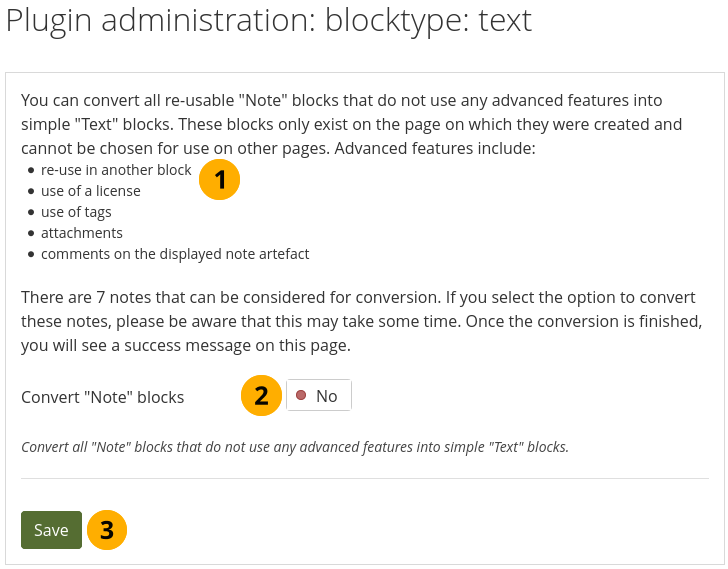
Configure text settings¶
Mahara calculates how many notes can be converted. Notes with the following characteristics are included in the conversion process. Notes that:
have not been re-used in another block;
do not have a license attached;
do not use tags;
do not have any attachments;
have not received any comments.
Turn on the option Convert ‘Note’ blocks to convert all notes.
Click the Save button to start the conversion process. This may take some time depending on how many notes are to be converted.
See also
If you have a large site, the conversion of notes to text may take a very long time. It can be beneficial to use the command-line script.
11.8.1.6. Blocktype: Wall¶
You can limit the number of characters that are allowed for wall posts in this configuration setting. Existing posts will not be changed.
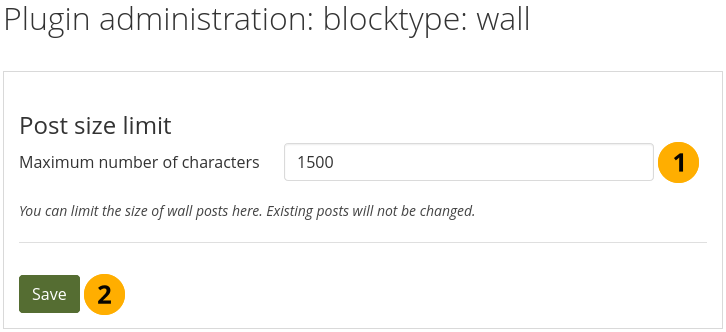
Configure wall settings¶
Choose the maximum number of characters for your wall posts.
Click the Save button to keep your changes.
11.8.1.7. Blocktype: Watchlist¶
Set the delay in minutes until watchlist notifications are sent. This prevents that too many notifications are sent when lots of changes are made within a short time frame.
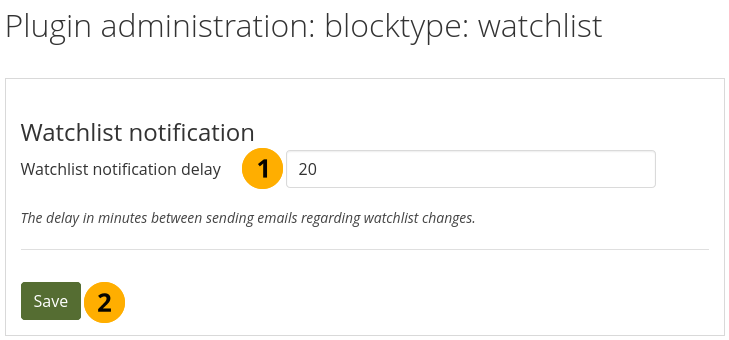
Configure the watchlist settings¶
Watchlist notification delay: Set the delay in minutes. Default setting: 20.
Click the Save button to keep your changes.
11.8.1.8. Artefact type: Comments¶
Turn comment ratings on to enable ratings in the comment section on artefacts and pages. You can change the look of the comment ratings as well as the scale.
Note
Ratings cannot be on their own. They require either a comment or a file attachment.
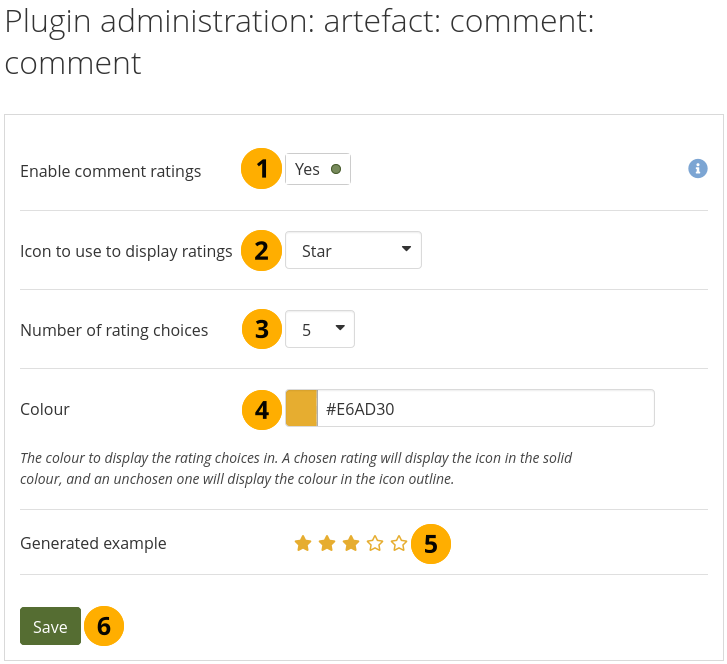
Enable comment ratings¶
Enable comment ratings: Switch to ‘Yes’ to enable comment ratings.
Icon to use to display ratings: Use the drop-down menu to select the icon that you want to use for your ratings. You can choose between:
Star
Heart
Thumbs up
Tick
Number of rating choices: Choose the scale that people will see when rating comments.
Note
If you change the number of rating choices, the ratings themselves will not be recalculated to fit that new scale.
Colour: Use the colour picker to select the colour for your icon or enter the hexadecimal color code.
Generated example: See a preview of what your comment ratings will look like.
Click the Save button to keep your changes.
11.8.1.9. Artefact type: File¶
You can configure a variety of options for uploading files:
Default account quota
Default group quota
Upload agreement
Resize images on upload
Profile picture size
Comments
Folder downloads
11.8.1.9.1. Default account quota¶
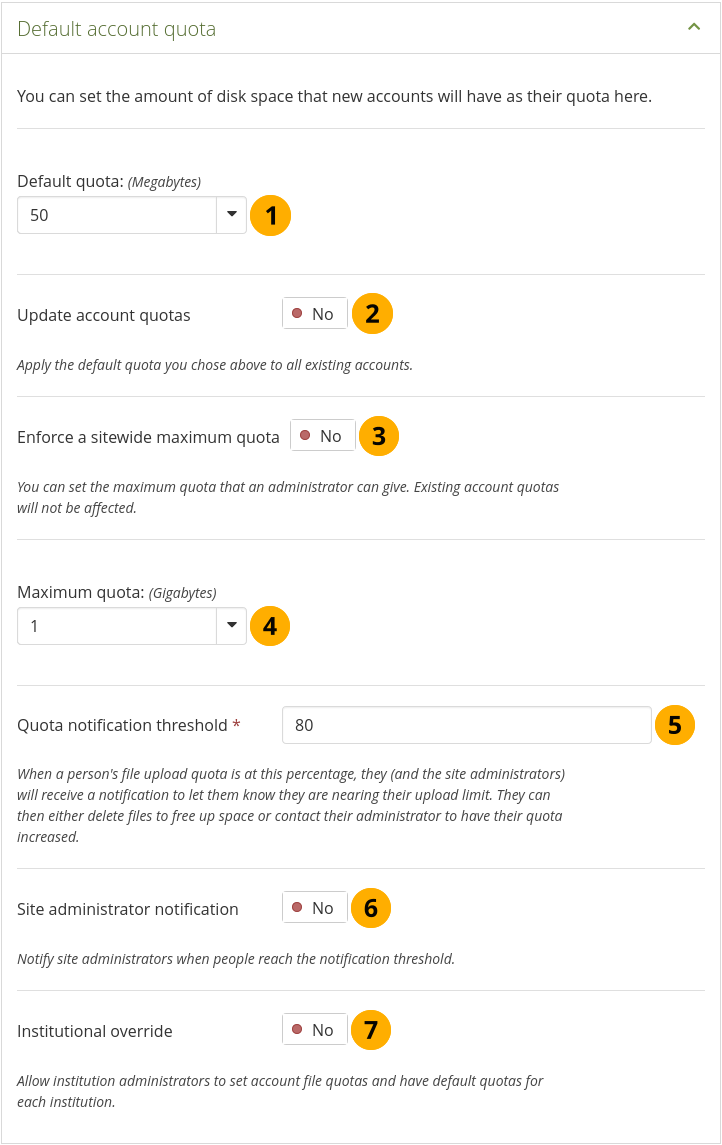
Configure the default account quota¶
Default quota: You can set the amount of disk space that new accounts will have as their quota. Existing account quotas will not be changed.
Update account quotas: Switch this option to ‘Yes’ if you want to update the file quota for existing accounts with the value under Default quota. Only then will they be updated.
Enforce a sitewide maximum quota: Switch to ‘Yes’ if you do not want an administrator to allocate more space than the Maximum quota.
Maximum quota: You can set the maximum quota that an administrator can give to an account holder. Existing account quotas will not be affected.
Quota notification threshold: Set a percentage for when an account holder receives a notification about reaching the upload limit for files. They can then decide to delete files to free up space or contact their site or institution administrator to request more space.
Site administrator notification: Switch to ‘Yes’ if the site administrator shall receive the quota notification emails to take action.
Institutional override: Switch this option to ‘Yes’ if you want to allow institution administrators to set account file quotas and have default quotas for each institution.
Click the Save button at the bottom of the page when you are finished making your changes or continue to the next section on this page.
11.8.1.9.2. Default group quota¶
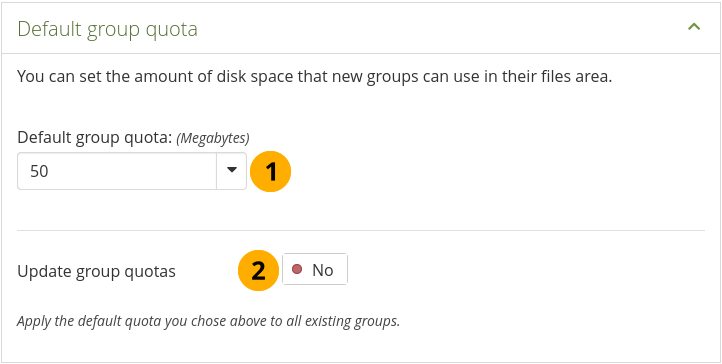
Configure the default group quota¶
Default group quota: You can set the amount of disk space that each group will have as its quota. Existing groups will not be affected.
Update group quotas: Switch to ‘Yes’ if you want to update the file quota for existing groups with the value under Default quota. Only then will they be updated.
Click the Save button at the bottom of the page when you are finished making your changes or continue to the next section on this page.
11.8.1.9.3. Upload agreement¶
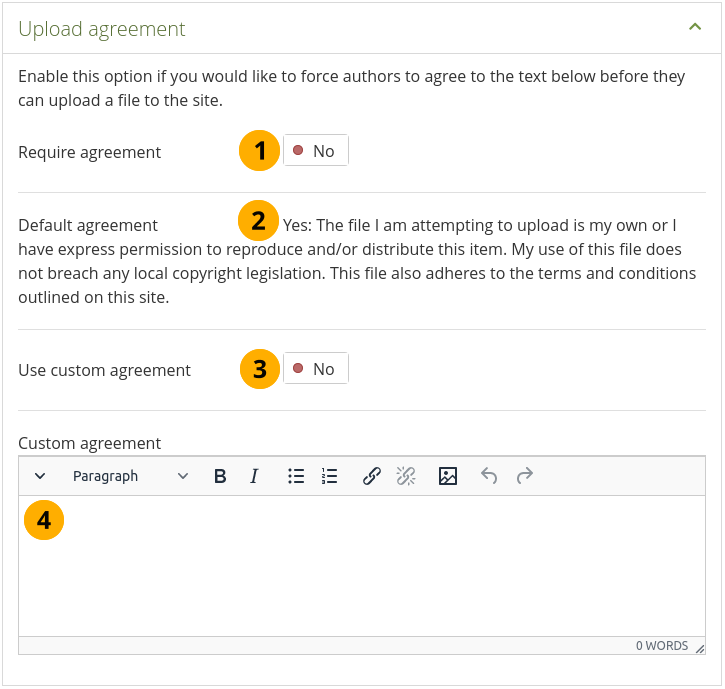
Configure the upload agreement¶
Require agreement: Switch to ‘Yes’ if you want to force people to agree to certain terms before they can upload a file to the site. They must accept this agreement before they are able to choose a file from their computer to upload to Mahara.
Default agreement: This is the default agreement that will be displayed if you selected the option Require agreement and if you don’t want to use your own custom agreement.
Use custom agreement: If you want to write your own upload agreement, switch this option to ‘Yes’ in addition to Require agreement.
Custom agreement: If you want to use a custom upload agreement, write it here.
Click the Save button at the bottom of the page when you are finished making your changes or continue to the next section on this page.
11.8.1.9.4. Resize images on upload¶
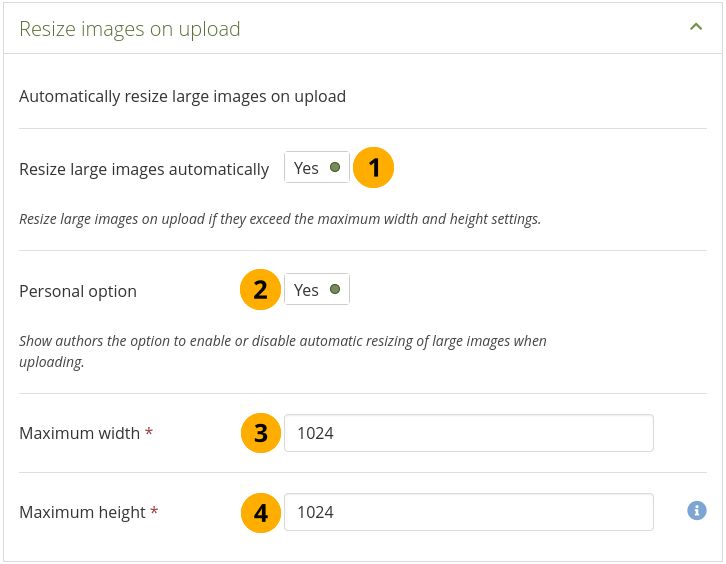
Configure the image resizing options¶
Resize large images automatically: Switch this option to ‘Yes’ to resize any image that is uploaded to the maximum width and height settings.
Personal option: Switch to ‘Yes’ if you want to display the option to resize images automatically in the account settings.
Maximum width: Choose the maximum width (in pixels) to which images will be resized upon uploading.
Maximum height: Choose the maximum height (in pixels) to which images will be resized upon uploading.
Click the Save button at the bottom of the page when you are finished making your changes or continue to the next section on this page.
11.8.1.9.5. Profile picture size¶
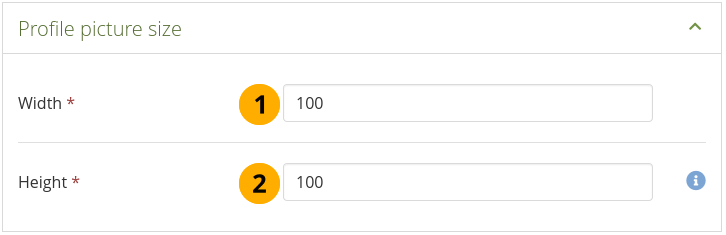
Configure the size of the profile pictures¶
Width: Choose the maximum width (in pixels) of the profile pictures.
Height: Choose the maximum height (in pixels) of the profile pictures.
Click the Save button at the bottom of the page when you are finished making your changes or continue to the next section on this page.
Note
All images uploaded to the profile pictures area will be resized to these dimensions if they are larger.
11.8.1.9.7. Folder downloads¶
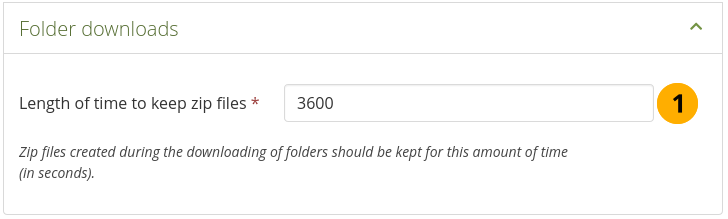
Configure the folder download settings¶
Length of time to keep zip files: Choose the amount of time for how long you want to keep the zip files on the server that are created during the folder download process. The default time frame is 3,600 seconds (1 hour).
Click the Save button when you are finished making your changes.
11.8.1.10. Artefact type: Internal - Profile¶
For profile information you can decide which fields someone must provide and which fields you can search on in the administration and elsewhere on the site.
See also
Add custom profile fields more via an addition to a local file in the Mahara code base.
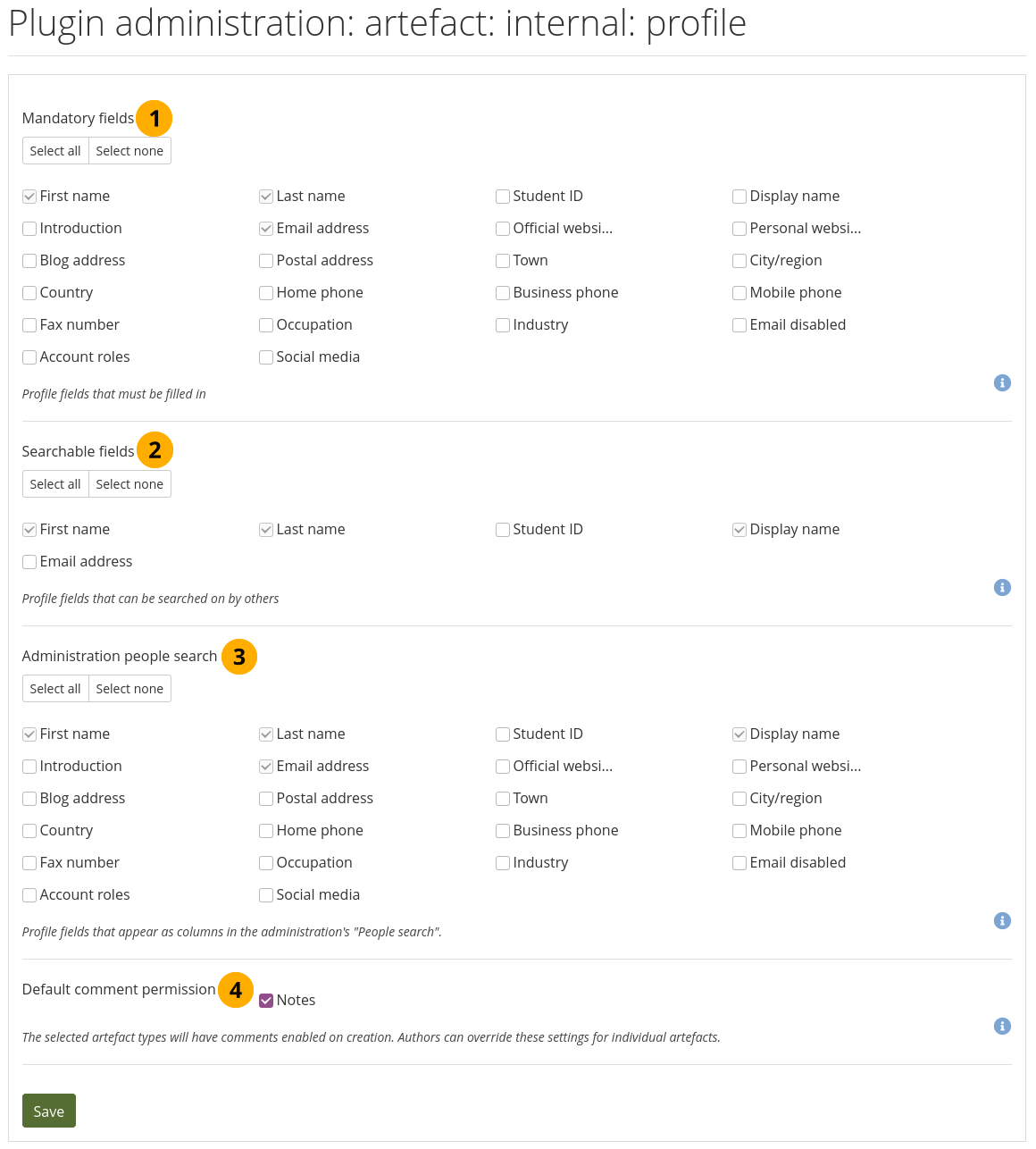
Choose mandatory and searchable profile fields¶
Mandatory fields: Select the fields that you wish everyone to fill in. Certain fields cannot be deselected.
Note
At the moment, you cannot unselect ‘Last name’ because it is needed when you use SAML for SSO purposes. If you do not use SAML and want to make the last name optional, you can change the code to accommodate your choice.
Searchable fields: Select the fields that can be searched on by others. Certain fields cannot be deselected.
Administration people search: Select the fields that you want to display in the People search table. The fields you select here are not exported to the CSV file though.
Default comment permissions: You can decide which artefacts shall have comments enabled per default. Currently, only ‘Notes’ are available. The default comment permissions for files are set in the plugin settings for files.
Note
Use the Select all and Select none buttons to select all profile fields at once or to clear your selection respectively.
Click the Save button to accept your changes.
11.8.1.11. Authentication: SAML¶
If you wish to use SAML authentication anywhere on your site, you can find all necessary information on your site’s metadata and certificate here.
Note
SimpleSAMLphp is a managed dependency that is included in Mahara, which makes the installation of SAML-based authentication methods easier.
You may need to install a few more dependencies manually. Please follow the on-screen instructions if that were the case.
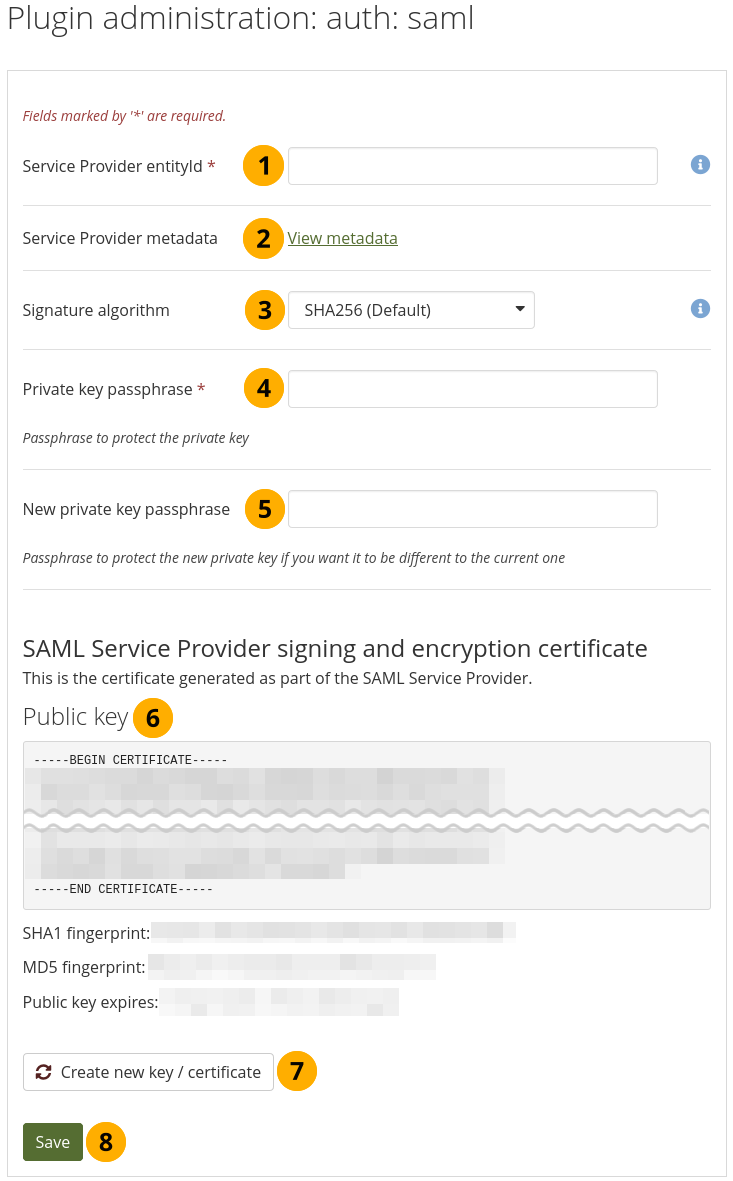
Prepare your site for SAML authentication¶
Service Provider entityId: This is the unique ID that identifies your Mahara instance to the Identity Provider, e.g. https://example.org/mahara. It is filled in automatically with the wwwroot of your instance. If it is incorrect, you can change it here.
Note
 The Service Provider entityID needs to be a valid URI, i.e. start with the protocol. If you upgrade your site from an earlier version of Mahara and did not have the protocol included, add it and create a new key so it can be added to the metadata. You will need to update your IdP with this new key for Mahara, i.e. provide the latest metadata.
The Service Provider entityID needs to be a valid URI, i.e. start with the protocol. If you upgrade your site from an earlier version of Mahara and did not have the protocol included, add it and create a new key so it can be added to the metadata. You will need to update your IdP with this new key for Mahara, i.e. provide the latest metadata.Service Provider metadata: The metadata link takes you to the page with your SAML metadata that you would need to give to the Identity Provider.
Signature algorithm: This is the algorithm that will be used to sign SAML requests. This makes it possible to use the SAML authentication with ADFS (Active Directory Federation Services). The following options are available:
SHA256 (Default)
SHA384
SHA512
Legacy SHA1 (Dangerous)
Warning
The SHA1 algorithm is only provided for backwards compatibility. Unless you absolutely must use it, it is recommended to avoid it and use at least SHA256 instead.
Private key passphrase: For added security, enter a passphrase to protect the private key.
Note
This passphrase now allows you to change your site name without that impacting the SAML certificate.
New private key passphrase: If you want to change the private key passphrase, you can do so here.
Public key: The public key is generated and rotated automatically. Typically, you would not need to copy it from here since you copy the entire metadata. It is displayed for verification purposes.
Click the Create new key / certificate button if you want to force the creation of a new public key.
Click the Save button to make your changes.
When you create a new key, the old certificate can still be used for an interim period of time until you delete it. This allows for a transition period until all IdPs use the new certificate.
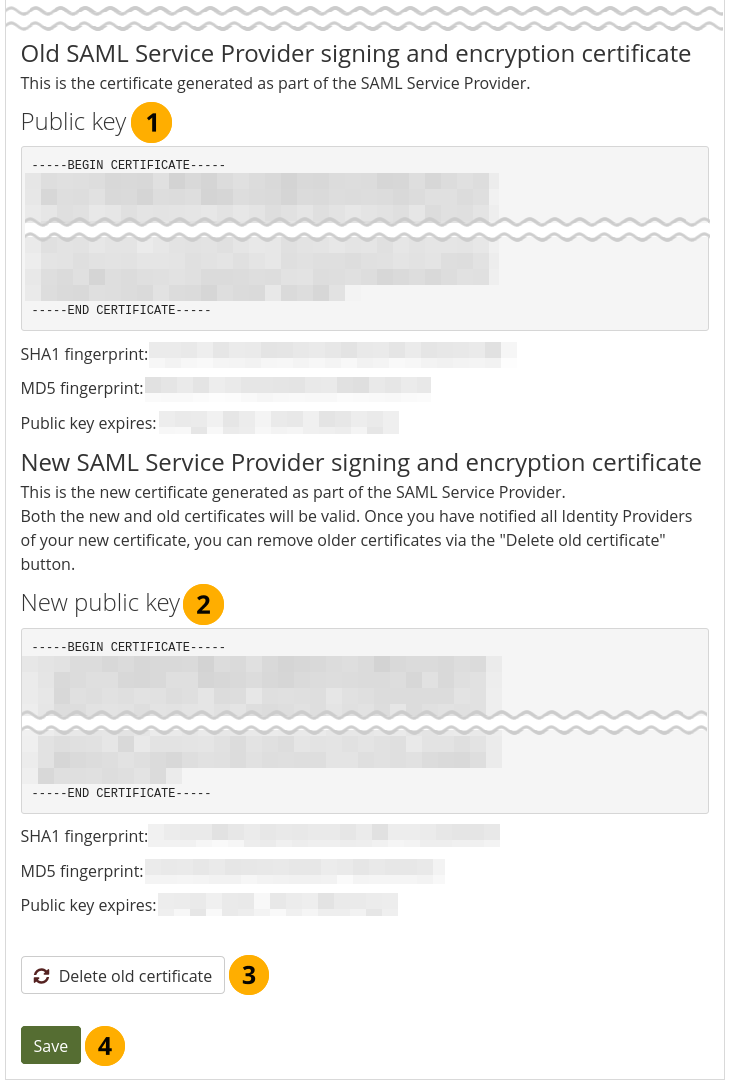
Rotate the SAML public key¶
Old SAML Service Provider signing and encryption certificate: The old certificate details are displayed and can be used until the certificate expires.
New SAML Service Provider signing and encryption certificate: The new certificate details are displayed and can be used immediately.
Click the Delete old certificate button to remove the old certificate when you are certain that no IdP is using it any more.
Click the Save button to make your changes.
You can view all Identity Providers that are set up on Mahara and delete them if needed.
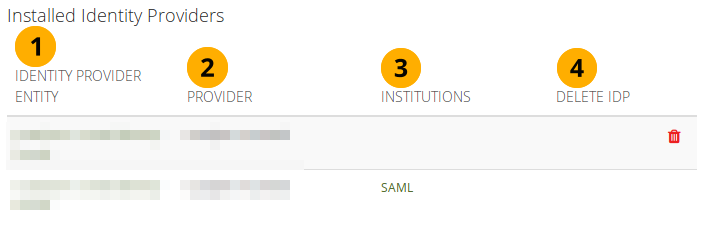
List all IdPs set up on the site¶
Identity Provider entity: Title of the Identity Provider’s authentication.
Provider: Name of the Identity Provider.
Institutions: Institution or institutions that use this IdP. The link takes you to the institution’s contacts page.
Delete IdP: Click the Delete button to remove the IdP that should not be used any more on the site. You see the button only for IdPs that are not used in any institution.
Tip
Some organisations may want to or need to generate a certificate with a higher bit rate, e.g. 4096bit. The encryption rate is handled by the server, and a PHP function accesses that value from /etc/ssl/openssl.cnf. If you use OpenSSL, the following would allow you to generate a certificate with a higher encryption:
Open /etc/ssl/openssl.cnf on your server.
Locate the line that includes
default_bit.Change the value to the one you want to use, e.g.
default_bit = 4096.Save the file.
Generate your SAML metadata.
11.8.1.12. Search: Elasticsearch 5/6¶
The regular Mahara search is limited to finding accounts and in certain places titles, descriptions, and tags of pages or collections. However, Mahara can be extended with full text search capabilities via Elasticsearch. Elasticsearch is is a powerful and extensible full text search engine that is also used for the learning analytics reporting in Mahara. It does require a Java server, e.g. Tomcat, to run.
Mahara still supports Elasticsearch 5 and 6, identified as ‘elasticsearch’ in the Plugin administration.
Note
If you are upgrading from a version of Mahara prior to Mahara 17.10 and you already had Elasticsearch in use, please take a look at the upgrade instructions for Elasticsearch 5/6. That documentation also provides information on how you can set up Elasticsearch on a computer for development purposes.
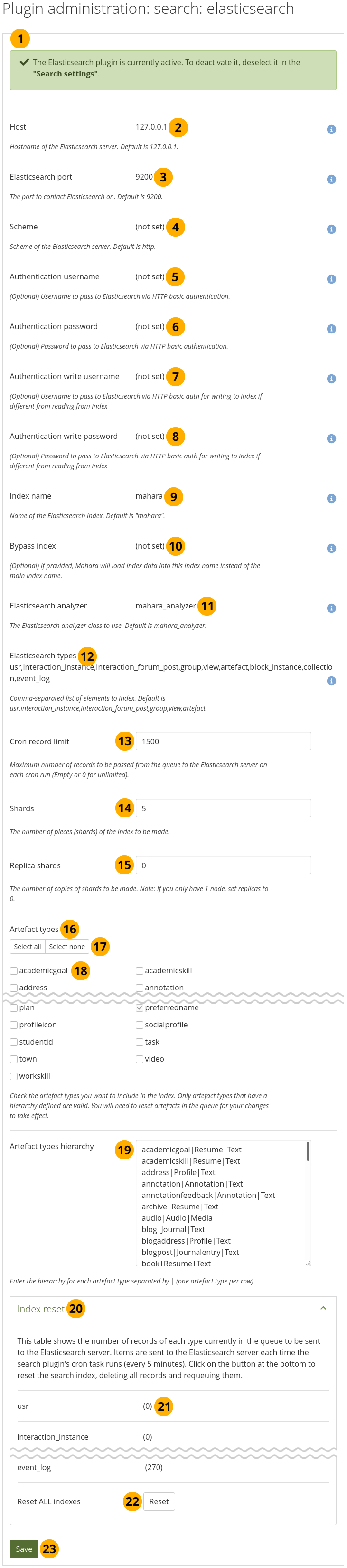
Configure the Elasticsearch plugin¶
The majority of the Elasticsearch configuration must be done on the server. This page displays that information, but does not allow you to set many configuration values.
At the top of the screen you see the overall status of Elasticsearch.
Host: The hostname of the Elasticsearch server. The default is
127.0.0.1.Elasticsearch port: The port used by Elasticsearch. The default is
9200.Scheme: Whether to use
httporhttps. Preferred ishttpsfor added security.Authentication username: The username required for the specific Elasticsearch index for this site to access information. This value is optional. It is only required when you have multiple sites accessing one Elasticsearch cluster.
Authentication password: The password used to secure the ‘Authentication username’. This value is optional.
Authentication write username: The username for writing to the search index. This value is optional.
Authentication write password: The password used to secure the ‘Authentication write username’. This value is optional.
Index name: The name of the search index. The default is ‘mahara’.
Bypass index: This index can be used to load data in instead of the main one. This value is optional.
Elasticsearch analyzer: The analyzer class. The default is ‘mahara_analyzer’.
Elasticsearch types: A comma-separated list of all the elements that Elasticsearch indexes. The default values are
usr, interaction_instance, interaction_forum_post, group, view, artefact.Cron record limit: Decide on the maximum number of records to be passed from the queue to the Elasticsearch server on each cron run. An empty field or
0means that there is no limit.Note
If you use Elasticsearch for development purposes on a computer, choose a small number, e.g.
1,500.Shards: The number of pieces that the index makes. The default is
5.Replica shards: The number of copies of the shards. If you only have one node, set this value to
0, e.g. when you run Elasticsearch on a development computer connecting to a local Elasticsearch setup.Artefact types: The artefact types that you want to include in the search index. Only artefact types that have a hierarchy defined below are valid. You will need to reset artefacts in the queue below for your changes to take effect.
Click the Select all or Select none buttons if you want to change your mind about the current selection quickly.
Select individual artefact types that you want to include into or exclude from the indexing.
Artefact types hierarchy: Enter the hierarchy for each artefact type that you selected separated by
|(a pipe). Place each artefact type on a row by itself.
Note
The first item is the artefact type, the second item is the category to which it belongs. This is an additional filter option. The third item is the main type, i.e. the tabs on the search result page.
Index reset: View the number of records of each type currently in the queue to be sent to the Elasticsearch server. Items are sent to the Elasticsearch server each time the search plugin’s cron task runs (every 5 minutes).
Each type is listed with the number of records not yet processed.
Reset ALL indexes: Click the Reset button to clear the search index and thus deleting all records and requeuing them. This also saves any changes you made on this page.
Click the Save button to accept your changes.
See also
You can find more information about Elasticsearch in Mahara on the wiki.
11.8.1.13. Search: Elasticsearch 7¶
Support for Elasticsearch 7 was introduced in Mahara 22.04. It is still possible to use Elasticsearch 5 or 6, but since they are not supported any more, it is recommended that you upgrade.
The regular Mahara search is limited to finding accounts and in certain places titles, descriptions, and tags of pages or collections. However, Mahara can be extended with full text search capabilities via Elasticsearch. Elasticsearch is is a powerful and extensible full text search engine that is also used for the learning analytics reporting in Mahara. It does require a Java server, e.g. Tomcat, to run.
11.8.1.13.1. General Elasticsearch 7 settings¶
The settings for Elasticsearch 7 resemble those for Elasticsearch 5 and 6. Some enhancements were made to requeue items and see the status of the cluster.
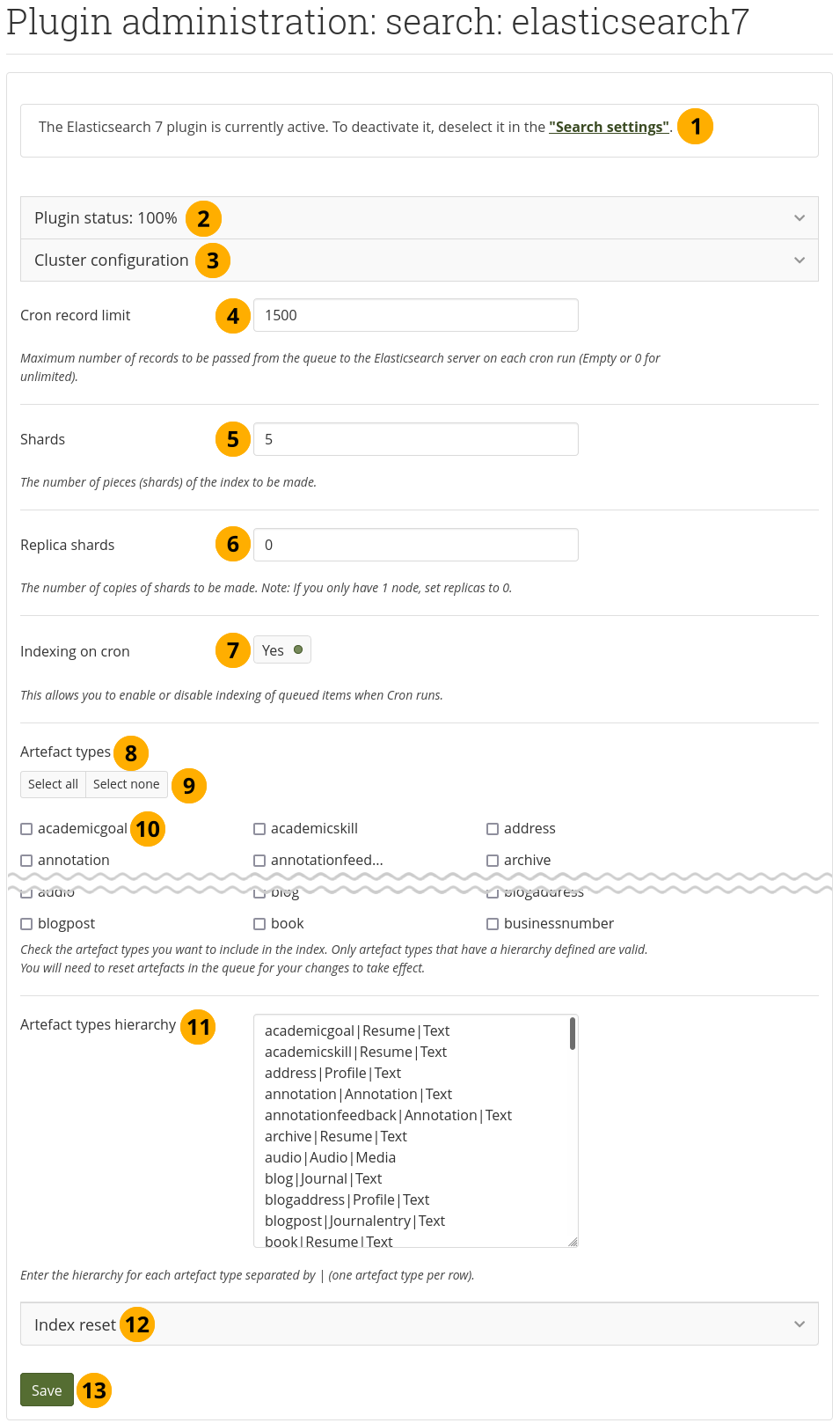
Configure the Elasticsearch 7 plugin¶
Statement on whether the plugin is currently in use and where to change it in the Site settings.
Plugin status: Items that give a quick overview of the Elasticsearch 7 plugin status.
Cluster configuration: Items that are configured on the server for the Elasticsearch 7 cluster configuration.
Cron record limit: Decide on the maximum number of records to be passed from the queue to the Elasticsearch server on each cron run. An empty field or
0means that there is no limit.Note
If you use Elasticsearch for development purposes on a computer, choose a small number, e.g.
1,500.Shards: The number of pieces that the index makes. The default is
5.Replica shards: The number of copies of the shards. If you only have one node, set this value to
0, e.g. when you run Elasticsearch on a development computer connecting to a local Elasticsearch setup.Indexing on cron: Decide whether you want the indexing to happen automatically.
Artefact types: The artefact types that you want to include in the search index. Only artefact types that have a hierarchy defined below are valid. You will need to reset artefacts in the queue below for your changes to take effect.
Click the Select all or Select none buttons if you want to change your mind about the current selection quickly.
Select individual artefact types that you want to include into or exclude from the indexing.
Artefact types hierarchy: Enter the hierarchy for each artefact type that you selected separated by
|(a pipe). Place each artefact type on a row by itself.
Note
The first item is the artefact type, the second item is the category to which it belongs. This is an additional filter option. The third item is the main type, i.e. the tabs on the search result page.
Index reset: Items relating to the resetting of the Elasticsearch 7 index reset options.
Click the Save button to accept your changes.
11.8.1.13.2. Plugin status¶
See the status of the Elasticsearch 7 plugin.
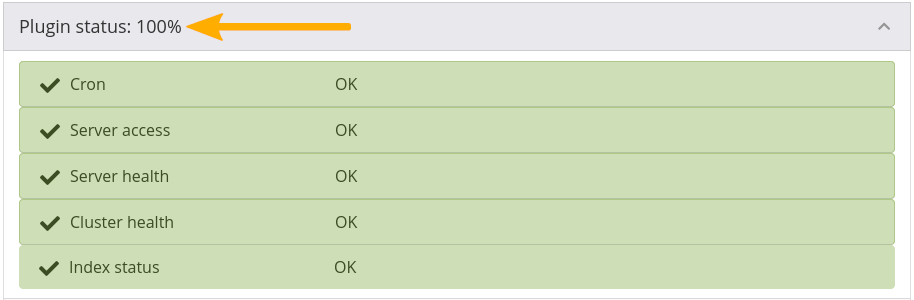
See the status of the Elasticsearch 7 plugin¶
You can quickly check if the plugin is working or which parts you may need to investigate. The overall percentage of everything fully functioning is provided.
The plugin status provides information on:
Runing of the cron
Server access for Elasticsearch to Mahara
Server health: If the server is running
Custer health: If the Elasticsearch cluster is running
Index status: If there are any issues with the Elasticserach index
11.8.1.13.3. Cluster configuration¶
The access to the Elasticsearch cluster is configured on the server so that site administrators don’t change settings accidentally.
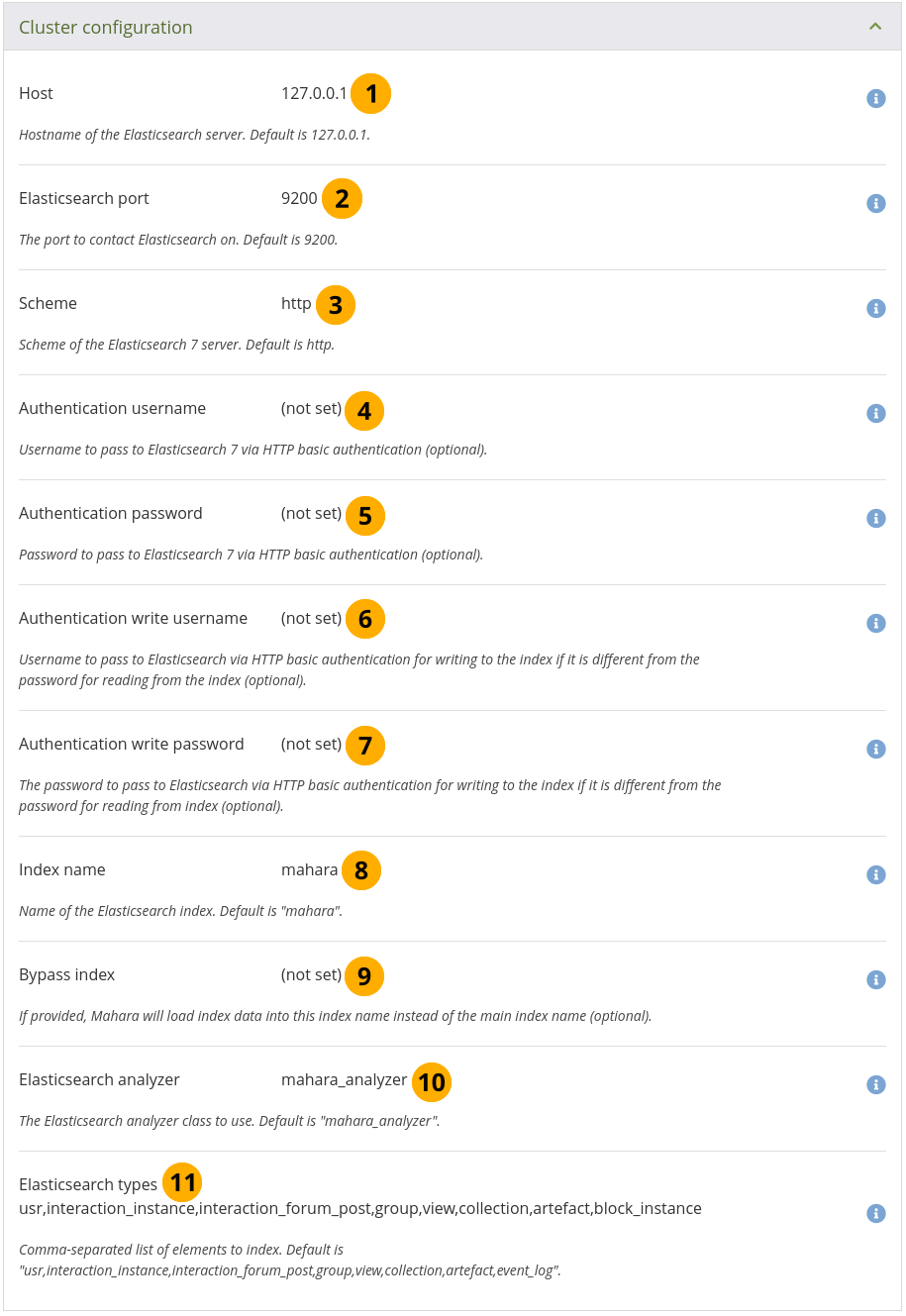
View the cluster configuration of Elasticsearch 7¶
Host: The hostname of the Elasticsearch server. The default is
127.0.0.1.Elasticsearch port: The port used by Elasticsearch. The default is
9200.Scheme: Whether to use
httporhttps. Preferred ishttpsfor added security.Authentication username: The username required for the specific Elasticsearch index for this site to access information. This value is optional. It is only required when you have multiple sites accessing one Elasticsearch cluster.
Authentication password: The password used to secure the ‘Authentication username’. This value is optional.
Authentication write username: The username for writing to the search index. This value is optional.
Authentication write password: The password used to secure the ‘Authentication write username’. This value is optional.
Index name: The name of the search index. The default is ‘mahara’.
Bypass index: This index can be used to load data in instead of the main one. This value is optional.
Elasticsearch analyzer: The analyzer class. The default is ‘mahara_analyzer’.
Elasticsearch types: A comma-separated list of all the elements that Elasticsearch indexes. The default values are
usr, interaction_instance, interaction_forum_post, group, view, artefact.
11.8.1.13.4. Index reset¶
This section shows how many records are currently in the Elasticsearch index, and how many are queued for indexing. Typically, the cron runs every five minutes and puts items into the index. In Elasticsearch 7 you can reset individual item types and thus don’t have to reset all indexes, which saves times especially on large sites.
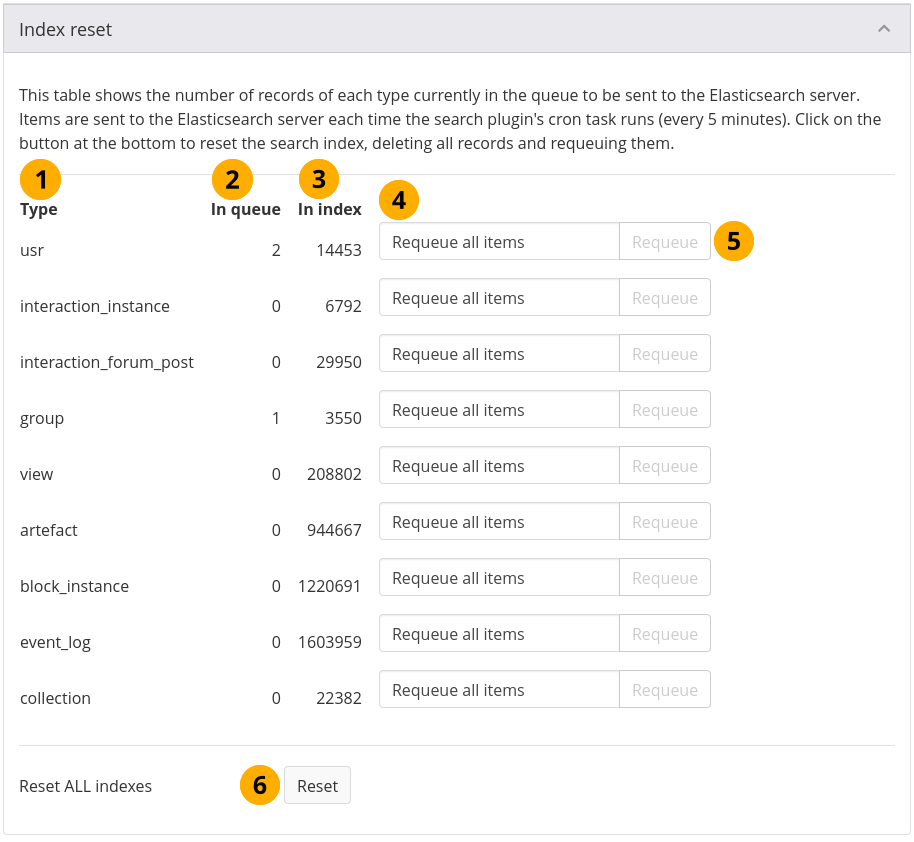
Configure the Elasticsearch 7 plugin¶
Type: The item type available for indexing.
usr: Personal information of people who have accounts, such as name
interaction_instance: The title and description of forums
interaction_forum_post: The content of forum posts
group: Information about groups, such as group name and description
view: title and description of pages
artefact: Information about artefacts, such as title, description, or full content, depending on the artefact type
block_instance: Information about the blocks, e.g. on which pages they are used.
event_log: Information that is stored in the event log
collection: Title and description of collections
In queue: The number of items awaiting to be indexed for each type.
In index: The number of items that are in the index for each type.
Type the number of the event into the field if you only want to requeue something specific.
Note
For example, if you had a problem with a particular page that was not indexed correctly, you can specify that without needing to reindex all the other pages. In this case, find the Mahara ID for the page by going looking at its URL or if you use cleanr URLs, click the ‘Edit’ button because the page ID is always displayed in ‘Edit’ mode. Then enter that number in this field.
Click the Requeue button next to a type to re-index either all items that are already in the index for this particular type or the specific item that you want to requeue.
Click the Reset button if you want to reset all indexes. Note: This will take several hours on large sites, and the items are not available in the fulltext search while they are being indexed.
11.8.1.14. Search: Internal search¶
If your site has a lot of accounts and uses a PostgreSQL database, people searches will be faster with exact people searching enabled. The setting will still work with MySQL databases, but it is unlikely that it increases search performance significantly.
The advantage of the exact people search is that if you have 20 people with the first name ‘Percy’ but different last names, you may find the person you are looking for more quickly because you can search for ‘Percy Pearle’ and the result list will not show ‘Percy Pearl’, ‘Percy Sutter’, ‘Percy Townsend’ etc.
However, partial matches on profile fields will not return results, so if for example you have someone called ‘Percy’, then typing ‘Perc’ into the search box will not find that person any more.
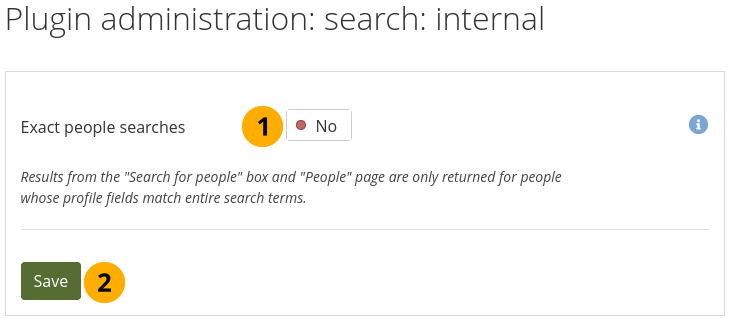
Configure the internal search plugin¶
Exact people searches: Switch this option to ‘Yes’ if you want to enable exact people searches.
Click the Save button to keep your changes.
11.8.1.15. Interaction: Forum¶
The post delay setting determines the time (in minutes) that group members have for editing their forum posts before they are mailed out. Once a forum post has been mailed and further edits are made, the date, time and editor are mentioned in the post.

Set the edit time before the forum post is finalised¶
Post delay: Set the time in minutes before a post is finalised and further edits are marked as such.
Click the Save button to keep your changes.
11.8.1.16. Module: LTI¶
You can activate the LTI API in order to use the LTI integration.
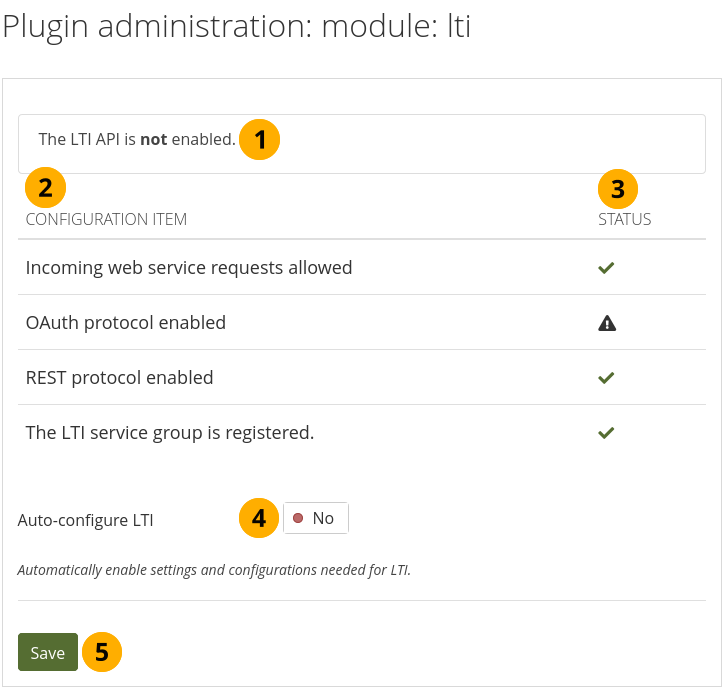
Configure the LTI plugin¶
The message lets you know whether the LTI functionality is enabled or not.
Configuration item: List of the configuration items for LTI.
Status: Displays which configuration items are ready to be used and which ones are not.
Auto-configure LTI: Switch to Yes if you want all settings to be made automatically.
Note
Once the auto-configuration was successful, you do not see this option any more. You can bring it back by making a change in the Web services section manually.
Click the Save button to save your changes.
11.8.1.17. Module: LTI Advantage¶
You can activate the LTI API in order to use the LTI integration.
Note
LTI Advantage is an experimental feature and has not yet been tested with LMS other than Brightspace.
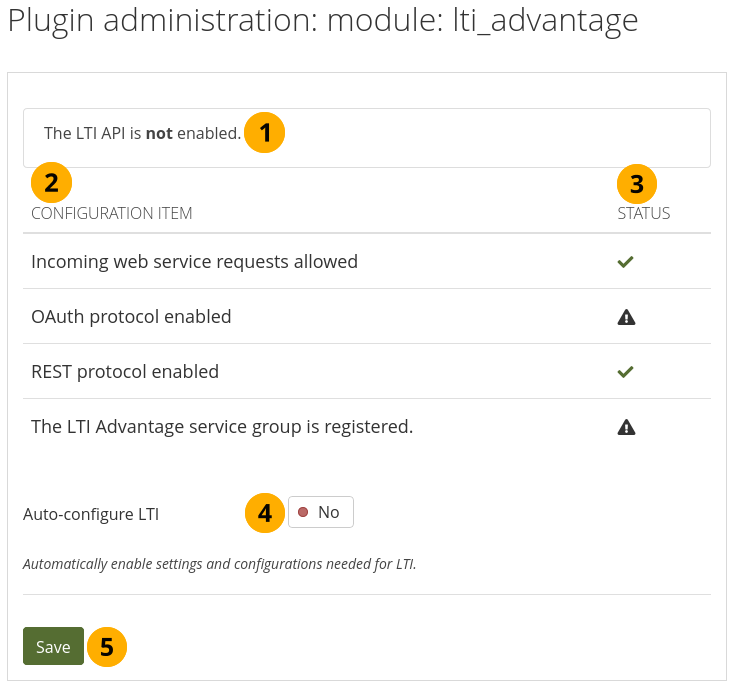
Configure the LTI Advantage plugin¶
The message lets you know whether the LTI functionality is enabled or not.
Configuration item: List of the configuration items for LTI Advantage.
Status: Displays which configuration items are ready to be used and which ones are not.
Auto-configure LTI: Switch to Yes if you want all settings to be made automatically.
Note
Once the auto-configuration was successful, you do not see this option any more. You can bring it back by making a change in the Web services section manually.
Click the Save button to save your changes.
11.8.1.18. Module: Mobile API¶
You can activate the mobile API in order to use ‘Mahara Mobile’, the new Mahara app.
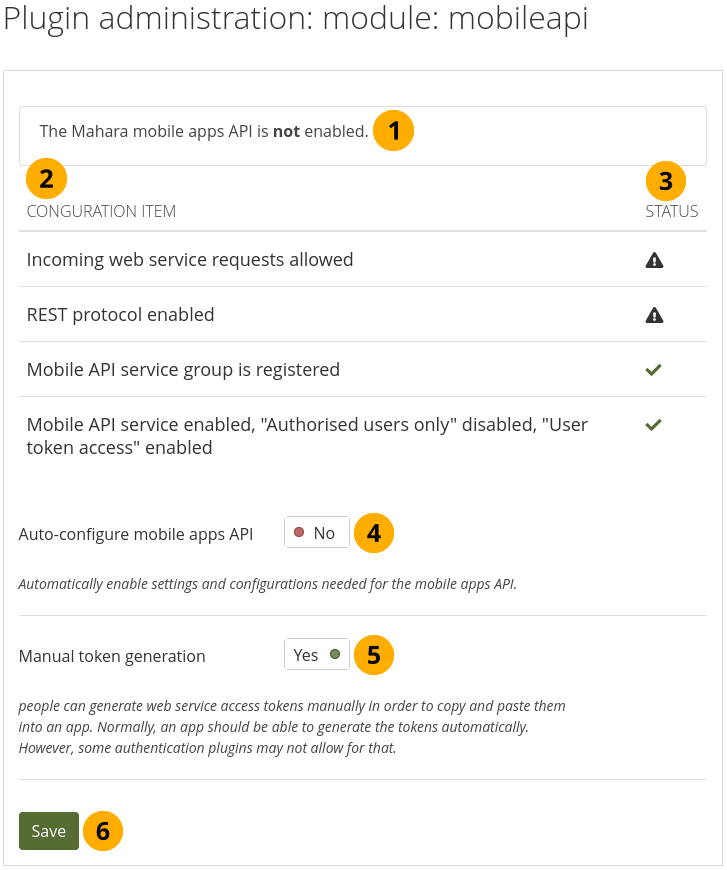
Configure the mobile API¶
The message lets you know whether the mobile apps API is enabled or not.
Configuration item: List of the configuration items for the mobile apps API.
Status: Displays which configuration items are ready to be used and which ones are not.
Auto-configure mobile apps API? Switch to Yes if you want all settings to be made automatically.
Note
Once the auto-configuration was successful, you do not see this option any more. You can bring it back by making a change in the Web services section manually.
Manual token generation: Switch to Yes if you want to allow your people to create the initial app token manually. This is only needed if the authentication method does not support the token generation. This is the case with MNet for example.
Click the Save button to save your changes.
11.8.1.19. Module: Monitor¶
Configure when you want to be alerted to failures in the cron job in an external monitoring software. You do not receive an alert in Mahara itself, but can use the CLI scripts to hook into your infrastructure monitoring tool.
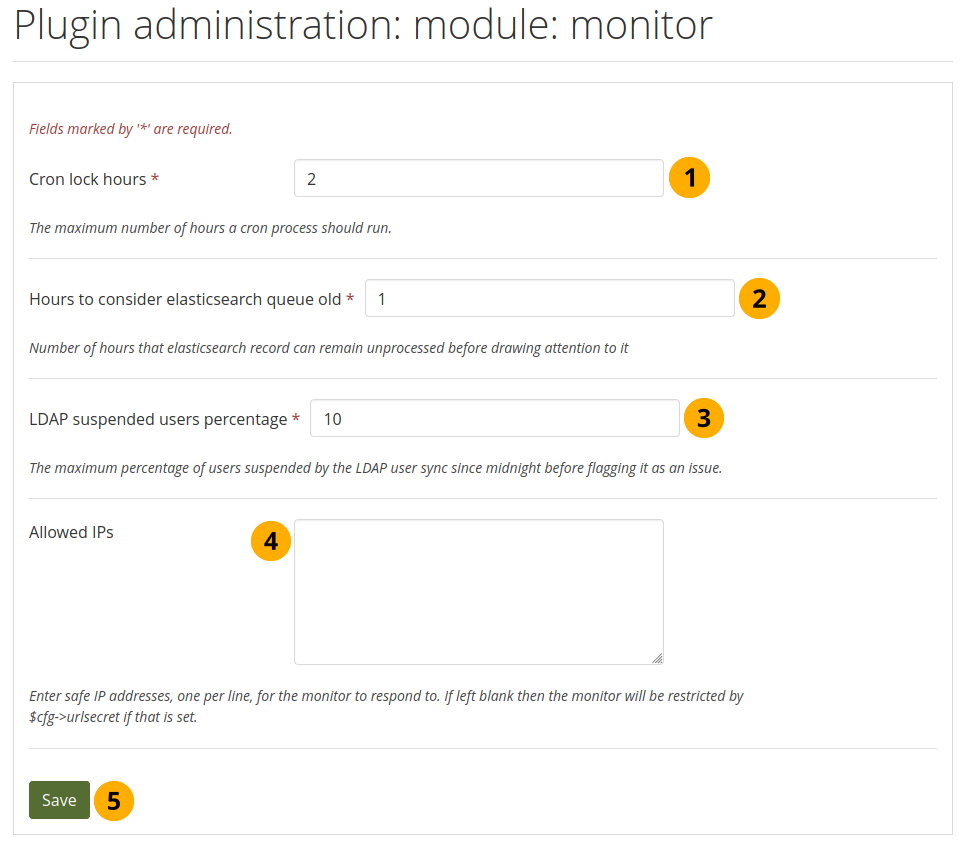
Configure the cron job monitor plugin¶
Cron lock hours: Enter a whole number for the maximum number of hours that a cron process should run before you are alerted to it failing. Default value: 2.
Hours to consider Elasticsearch queue old: Enter a whole number to indicate after how many hours you want to be alerted when an entry in Elasticsearch hasn’t been processed. Default value: 1.
LDAP suspended users percentage: Enter a whole number that indicates how many accounts can be suspended since midnight before you receive an alert. Default value: 10.
Allowed IPs: List the IP addresses that can bypass the urlsecret config variable in order to access the cron job monitor.
Click the Save button to accept your changes.
See also
You can view results on the ‘Monitor’ page and export them as CSV file if you do not have an external dashboard.
11.8.2. HTML filters¶
Administration menu → Extensions → HTML filters
Mahara uses HTML Purifier to filter out malicious code that could threaten the security of the system. If you have code, e.g. iFrames or JavaScript that you wish to use and that otherwise gets filtered out, you will have to write a filter to circumvent that. Filters should always be specific to their purpose and not give ‘carte blanche’ to ensure security as much as possible.
Mahara already comes with a number of installed filters. Others can be uploaded and then installed. If you have created a new set of HTML filters, you can install them by unzipping the files into the folder /htdocs/lib/htmlpurifiercustom and then click the Install button.
Custom filters for iFrames that allow the embedding of media content such as YouTube and WikiEducator allow authors to grab the URL of the page on which the media is displayed instead of having to find the actual embed code.
Note
You do not necessarily require bespoke filters for media that you wish to embed via <iframe> embed code. If you are happy to use the original embed code, you can add it to the list of allowed iframe sources.
If you wish to be able to paste the URL instead (like for a YouTube video), then you would need a bespoke filter.
11.8.3. Allowed iframe sources¶
Administration menu → Extensions → Allowed iframe sources
This feature allows you as site administrator to specify the base URLs for media that you want authors to be able to embed. These iframes are then considered safe and will not be stripped out of a Text or Note block, the External media block or a journal entry where you can use them. You do not have to write bespoke filters for using these iframe sources.
The administrator interface allows you to add and manage these sources. Mahara already comes with a number of built-in iframe sources that you can take as examples.
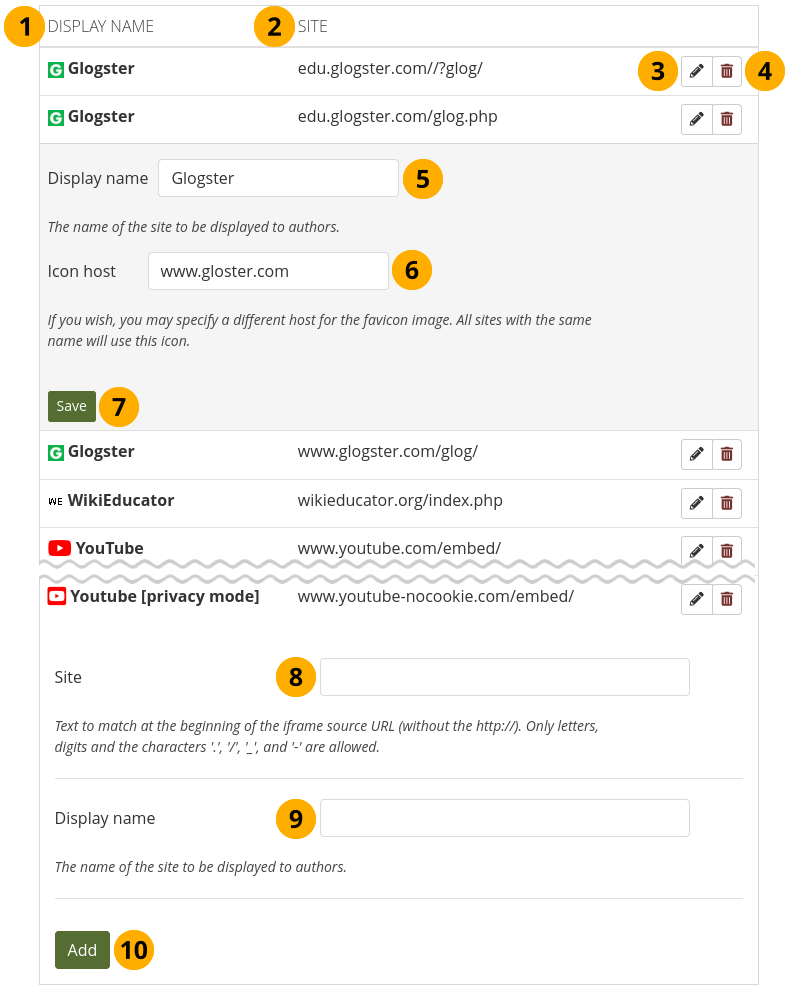
Add and edit allowed iframe sources¶
Display name: What the author will see in the external media block.
Site: The base URL of the iframe code.
Click the Edit button to update the display name of an existing iframe source or the favicon source.
Click the Delete button to remove an existing iframe source.
Display name: Change the display name of an existing iframe source here after having clicked the Edit button .
Icon host: Choose the base URL where the favicon can be found for the site that you are updating in case it is not fetched automatically.
Click the Save button to keep your changes for this site.
Site: Add a new iframe source by entering its base URL here. Please make sure to leave out the
https://. Only letters, digits and. / - _are allowed.Display name: Choose a display name for your iframe source. Typically, this is the name of the site that hosts the external content.
Click the Add button to place your new site into the list of allowed iframe sources. If the favicon does not display, edit your site and specify the icon host as per Step 6.
Note
Some sites can be reached via a variety of URLs, e.g. GoogleApps, Glogster. You need to provide all possible base URLs to ensure that the iframes are displayed. If you give the individual sites of one provider the same name, it will only show up once in the list of iframe sources in the external media block and not clutter the space unnecessarily.
11.8.4. Clean URLs¶
Administration menu → Extensions → Clean URLs
You can configure your site to use human-readable URLs for personal profiles, groups and (group) portfolio pages. For example:
profile page: https://mahara.example.com/user/bob
portfolio page: https://mahara.example.com/user/bob/bobs-portfolio-page
group homepage: https://mahara.example.com/group/bobs-group
group portfolio page: https://mahara.example.com/group/bobs-group/an-interesting-group-page
This option allows you to create more memorable URLs.
See also
Please follow the configuration instructions on the wiki for enabling this feature on your site. You need access to the server to do so.
In the administration area you can generate clean URLs for existing accounts, groups, and pages. This is handy when you upgraded from an earlier version of Mahara or want to reset all custom URLs.
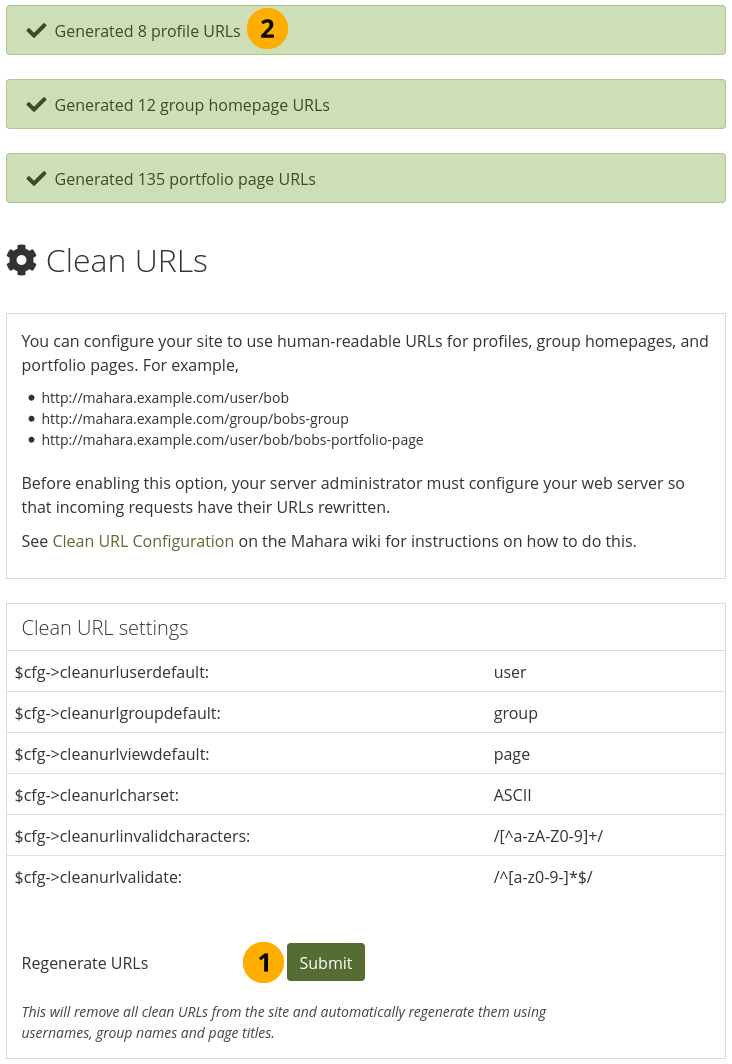
Regenerate clean URLs for existing accounts in bulk¶
Click the Submit button to regenerate clean URLs. Please beware that all existing clean URLs are lost.
You see the results of the action at the top of the screen.
Warning
If you generate clean URLs for all accounts from here, those who have already changed their URLs will lose their changes and links will be broken. We recommend you use this feature only when upgrading your Mahara site or when things have gone wrong with the clean URL generation.

11.8.1.9.6. Comments¶
Configure the default comment settings for different file types¶
Click the Select All button to mark all file types.
Click the Select none button to clear your selections of the checkboxes.
Default comment permission: Choose the artefact types which shall have comments enabled per default. Authors can override these settings for individual artefacts in the files area. You can enable comments for:
archive, i.e. compressed file
audio file
file
folder
image
profile picture
video file
Click the Save button at the bottom of the page when you are finished making your changes or continue to the next section on this page.